Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CONJUNCTIONS
Uploaded by
Tamara HernandezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CONJUNCTIONS
Uploaded by
Tamara HernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
A conjunction is a joining/linking word.
It joins/links
word,phrases,sentences,ideas and things together.
The simple, little conjunction are called coordinating
conjunctions.
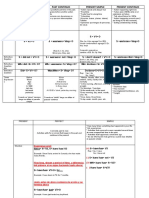
1) For
2) And
3) Nor
4) But
5) Or
6) Yet
7) so
Here are some example of coordinating conjunction in English and what they
do:
For
Presents rationale (they do not gamble or,smoke,for they are ascetics)
And
Presents non-contrasting item (s) or idea (s)
(they gamble and they smoke)
Nor
Presents a non-contrasting negative idea (they do not gamble, nor do they
smoke)
But
Presents a contrast or exception (they gamble, but they dont smoke)
Or
Presents an alternative item or idea (every day they gamble or they smoke)
Yet
Presents a contranst or exception (they gamble, yet they dont smoke)
So
Presents a consequence (he gambled well last night so he smoked a cigar to
celebrate)
Join words and groups of word of equal weight in a
sentence. There are six different pairs of correlative
conjunctions.
1) Eitheror
2) Not onlybut(also)
3) Neither..nor
4) Both..and
5) Whetheror
6) just asso
You either do your work or prepare for a trip to the office
Not only is he handsome,but he is also brilliant
Neither the basketball team nor the football team is doing
well
Both the cross country team and the swimming team are
doing well
Whether you stay or you go,its your decision
Just as many Americans love basketball,so many
canadians love ice hackey
A subordinating conjunctions (sometimes called a
dependent word or subordinator) comes at thee beginning
of a ssubrodinate (or Dependent) clause and establishes
the relatoinship between the dependent clause and the rest
of the sentence.It also turns the clause into something that
depends on the rest of the sentence for its meaning
He look to the stage as though he had been preparing for
this moment all his life
Because he loved acting, he refused to give up his dream
of being in the movies
unless we act now, all is lost
Notice that some of the subordinating
conjunctions in the table below-after, before,
since-are also prepositions, but as
subordinators they are being used to
subordinate the following clause to the
independent elemeat in seatencee
*after *if *though
*Although *if only *till
*As *in order that *unless
*As if *now that *until
*As long as *once *when
*As though *rather than *whenever
*Because *since *where
*Before *so that *whereas
*Even if *than *wherever
*Even though *that *while
You might also like
- PrepositionDocument25 pagesPrepositionFatimah Az Zahra100% (1)
- YÖKDİL guide to English grammar structuresDocument8 pagesYÖKDİL guide to English grammar structuresresearcher-690955No ratings yet
- CLAUSE Adverb Clause JSLDocument13 pagesCLAUSE Adverb Clause JSLoperation teknoNo ratings yet
- Hardly-Scarcely-Barely-No SoonerDocument6 pagesHardly-Scarcely-Barely-No SoonerheartvampireNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Nouns WorksheetDocument1 pageKinds of Nouns WorksheetClaive Rivas-Pangatongan100% (2)
- Vocabulary and Grammar Consolidation and Extension: Starter Unit Unit 1 Unit 6Document23 pagesVocabulary and Grammar Consolidation and Extension: Starter Unit Unit 1 Unit 6GeorginaNo ratings yet
- Stative Verbs ListingDocument6 pagesStative Verbs ListingBeatrice MedințuNo ratings yet
- Adjective ClausesDocument9 pagesAdjective ClausessulastriNo ratings yet
- Types of Conjunctions ExplainedDocument5 pagesTypes of Conjunctions ExplainedAbhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- Dependent WordsDocument1 pageDependent WordsMihály AleNo ratings yet
- Conjuctions SentenceDocument13 pagesConjuctions SentenceJosé Saúl Rivas MendozaNo ratings yet
- Types of German ConjunctionsDocument5 pagesTypes of German ConjunctionsLaura CristinaNo ratings yet
- Conjuctions Sentence Transformation Rephrasing Exercises TBL T 82295Document13 pagesConjuctions Sentence Transformation Rephrasing Exercises TBL T 82295Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: Hazırlayan: S. Beril YILMAZDocument13 pagesConjunctions: Hazırlayan: S. Beril YILMAZSkkkl KkkklNo ratings yet
- Adverbial ClauseDocument23 pagesAdverbial ClauseJulius RichardNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: A Conjunction Is A Joiner, A Word That Connects (Conjoins) Parts of A SentenceDocument19 pagesConjunctions: A Conjunction Is A Joiner, A Word That Connects (Conjoins) Parts of A Sentencediksha guptaNo ratings yet
- Adverb Clause: Aditya Yusta Kalpika Gilang NugrahaDocument23 pagesAdverb Clause: Aditya Yusta Kalpika Gilang NugrahaAdityaYustaKalpikaNo ratings yet
- Subj Adv ClausesDocument4 pagesSubj Adv ClausesmbalcellsNo ratings yet
- Adverb ClausesDocument19 pagesAdverb ClausesarturoNo ratings yet
- Estruturação Da Escrita em Lingua Inglesa: O Que É Necessário para Escrever Bem?Document11 pagesEstruturação Da Escrita em Lingua Inglesa: O Que É Necessário para Escrever Bem?bonamin9379No ratings yet
- English connectors guideDocument26 pagesEnglish connectors guidelondonfaidel6511No ratings yet
- Conjunctions: Hazırlayan: S. Beril YILMAZDocument13 pagesConjunctions: Hazırlayan: S. Beril YILMAZAndrea MuñozNo ratings yet
- ANGIE ZULAY REMOLINA ANZOLA AND LAURA VIVIANA BAYONA ORREGO: GRAMMAR TOPICS EXPLAINEDDocument23 pagesANGIE ZULAY REMOLINA ANZOLA AND LAURA VIVIANA BAYONA ORREGO: GRAMMAR TOPICS EXPLAINEDlaura bayona100% (1)
- Pex 08 02Document14 pagesPex 08 02Antonio YaksaNo ratings yet
- ConectoresDocument19 pagesConectoreswiston botinaNo ratings yet
- Unreal Time and SubjunctivesDocument17 pagesUnreal Time and SubjunctivesMilica StojkovićNo ratings yet
- Ingles 4Document7 pagesIngles 4María BonoNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: Translation Department 2 Year / 4 Semester 2022-2023Document30 pagesConjunctions: Translation Department 2 Year / 4 Semester 2022-2023rayanNo ratings yet
- TransitionsDocument2 pagesTransitionsapi-261436805No ratings yet
- Subordinating ConjunctionsDocument1 pageSubordinating ConjunctionsValter Pinheiro LimaNo ratings yet
- FUTURODocument16 pagesFUTUROrodrigoNo ratings yet
- Adverb Time Clauses - TheoryDocument2 pagesAdverb Time Clauses - TheoryAlice MihalceaNo ratings yet
- Future ContinuousDocument6 pagesFuture Continuous3A EDUARDO ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)Document7 pagesConjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)dicky ardiasyahNo ratings yet
- Cuadro EsquematicoDocument2 pagesCuadro EsquematicoAna PortalesNo ratings yet
- Futur Proche vs. Futur Simple Differences Between French and EnglishDocument3 pagesFutur Proche vs. Futur Simple Differences Between French and EnglishsilverpenNo ratings yet
- Why Are These Verbs Troublesome?: Lie / Lay Sit / Set Rise / RaiseDocument32 pagesWhy Are These Verbs Troublesome?: Lie / Lay Sit / Set Rise / RaiseAnggi Lestari EffendiNo ratings yet
- Clase 1Document11 pagesClase 1n6kh2zj2gwNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions of ContrastDocument4 pagesConjunctions of ContrastEstefania Alzate MontesNo ratings yet
- Doubts in EnglishDocument18 pagesDoubts in EnglishSheylaMoralesNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple V/S Present Perfect Continuous Subject: English Grade: 1 MediosDocument15 pagesPresent Perfect Simple V/S Present Perfect Continuous Subject: English Grade: 1 Mediostere.ramosNo ratings yet
- Le Joual Quebec Slang WikiDocument12 pagesLe Joual Quebec Slang WikiThe CheetahNo ratings yet
- Have You Ever o Do You Ever - AdicionalDocument168 pagesHave You Ever o Do You Ever - AdicionalmartinNo ratings yet
- Akad Perjanjian KerjaDocument5 pagesAkad Perjanjian KerjasheylaelmalayNo ratings yet
- M!L!H!SD! !!!!:!! ® 'I F ! A!m W Ew!!!p!!!!!!!!!!!! A!! F!!!!!!!!! ! ! !!! LLLTLLDocument28 pagesM!L!H!SD! !!!!:!! ® 'I F ! A!m W Ew!!!p!!!!!!!!!!!! A!! F!!!!!!!!! ! ! !!! LLLTLLAngelNo ratings yet
- Primary Verb ChartDocument3 pagesPrimary Verb Chartromeroflaviax01No ratings yet
- Ingles 2Document6 pagesIngles 2dounorquixNo ratings yet
- Students The present simple and the present simple continuous - CopyDocument6 pagesStudents The present simple and the present simple continuous - CopyDương 10 Hoá TiêuNo ratings yet
- Clase de Ingles UnoDocument13 pagesClase de Ingles UnoCecilia LayusNo ratings yet
- A An Any Another Other WhatDocument8 pagesA An Any Another Other WhatCt Fairuz HananiNo ratings yet
- Conjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)Document10 pagesConjunctions: A. Coordinating Conjunctions (Fanboys)KiangXintianNo ratings yet
- Learn about "Be Going ToDocument13 pagesLearn about "Be Going ToEti OrenjiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Notas de ClasesDocument13 pagesPresent Perfect Notas de ClasesGarcia Becerra JaquelineNo ratings yet
- Espresso English- Ask-the-Teacher-LessonsDocument19 pagesEspresso English- Ask-the-Teacher-Lessonsjosenato1970No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Present Perfect: Ever, Never, and BeforeDocument1 pageLesson 1: The Present Perfect: Ever, Never, and BeforeDiana Carolina Figueroa MendezNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument22 pagesFuture TensesAlexandra EvaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Reported Speech - StatementsDocument3 pages1 - Reported Speech - StatementsJohnyNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Prepared by Miss Ellie Blossom UtoniumDocument45 pagesGrammar: Prepared by Miss Ellie Blossom UtoniumEllie AJ KinsonNo ratings yet
- Conjunction SDocument33 pagesConjunction SRavina WarkadNo ratings yet
- Adverbial ClausesDocument3 pagesAdverbial ClausesSalwa SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- ConjunctionDocument10 pagesConjunctionRegitaNo ratings yet
- Tense and Aspect: Perfective Aspect Progressive Aspect Present Tense Past TenseDocument6 pagesTense and Aspect: Perfective Aspect Progressive Aspect Present Tense Past TenseLiljana DimeskaNo ratings yet
- Grammar & Reading Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesGrammar & Reading Cheat Sheetghada kamalNo ratings yet
- No Mistakes Grammar Bites, Volume VIII, Anxious and Eager, and Different From and Different ThanFrom EverandNo Mistakes Grammar Bites, Volume VIII, Anxious and Eager, and Different From and Different ThanNo ratings yet
- It’s a very exciting placeDocument11 pagesIt’s a very exciting placeMara Silveira Dias33% (3)
- Your English Pal Business English Lesson Plan Stress Student v1Document3 pagesYour English Pal Business English Lesson Plan Stress Student v1Yulia PetrishakNo ratings yet
- Food DrinksDocument22 pagesFood DrinksGerardo Aguirre HernandezNo ratings yet
- 147 Vocabulary Unit 3 3starDocument1 page147 Vocabulary Unit 3 3starTa Ma GlNo ratings yet
- Sow English Form 2 2024-25Document4 pagesSow English Form 2 2024-25Noraini Che YusohNo ratings yet
- Tense Simple Future Basic Use Form 1/ Verb + ? WH/H? - Form 2/ Non-Verb + ? WH/H? - Tense Time Expression ExamplesDocument5 pagesTense Simple Future Basic Use Form 1/ Verb + ? WH/H? - Form 2/ Non-Verb + ? WH/H? - Tense Time Expression Examplessavira salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: I. Chose The Correct Verb Form in AffirmativeDocument3 pagesSimple Present: I. Chose The Correct Verb Form in AffirmativeLalys CiaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 - VerbDocument28 pagesClass 6 - VerbjoshuaNo ratings yet
- 2011 04april Lesson GuideDocument151 pages2011 04april Lesson GuideShambhu SinghNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Formal LetterDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Formal LetterCristina SempereNo ratings yet
- Bilingv Scris 014Document3 pagesBilingv Scris 014Iulian PopaNo ratings yet
- ABCDocument33 pagesABCYanHongNo ratings yet
- Narrative Tenses Oktapodi WorksheetDocument2 pagesNarrative Tenses Oktapodi Worksheetvinca sherinNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR - Introductory 'There' and 'It' - OCR PDFDocument10 pagesGRAMMAR - Introductory 'There' and 'It' - OCR PDFAgustin Vila SánchezNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous TenseDocument9 pagesPresent Continuous TenseWMFILESNo ratings yet
- Right Form of Verb RulesDocument4 pagesRight Form of Verb RulesshakibNo ratings yet
- What's The News Today?: Pathway To English For Senior High School Grade XII General ProgramDocument22 pagesWhat's The News Today?: Pathway To English For Senior High School Grade XII General ProgramMaulana Surya NegaraNo ratings yet
- LP GrammarDocument5 pagesLP GrammarmayuashNo ratings yet
- Q1 ST 2019 No.1Document23 pagesQ1 ST 2019 No.1Janice Corañes0% (1)
- Plural of Nouns and AdjectivesDocument2 pagesPlural of Nouns and Adjectivesapi-546261830No ratings yet
- 1 First MeetingDocument2 pages1 First MeetingOksana PantiuchinaNo ratings yet
- Asking and Giving Suggestion RevisiDocument8 pagesAsking and Giving Suggestion Revisicantiq bangetNo ratings yet
- So Such Too EnoughDocument4 pagesSo Such Too EnoughKruveKruveNo ratings yet
- Adverbs or AdjectivesDocument13 pagesAdverbs or Adjectivescesar garciaNo ratings yet
- CEFR VocabularyDocument162 pagesCEFR VocabularyDennis JamesNo ratings yet
- Ge Module 1Document14 pagesGe Module 1Hilman MafaziNo ratings yet