Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ethical Issues in Business: Sexual Harassment and Just Wages
Uploaded by
JTupakOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethical Issues in Business: Sexual Harassment and Just Wages
Uploaded by
JTupakCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethical Issues and
Problems in
Business and the
Corporate World
CHAPTER V
Business is a productive human activity that
brings beneficial contribution to both people and
society.
Business produces employment, fair deals,
creativity, advancement of technology, customer
satisfaction, among others.
Ironically, however, business is also an activity
that provides an opportunity for some
unscrupulous people to take advantage of
others:
e.g. the abuse of fiduciary relationship
between employers
and employees and between the buyers and the
sellers
INTRODUCTION
1. SEXUAL HARASSMENT
WHAT IS SEXUAL
HARASSMENT?
This is an issue in the corporate world that
must be looked into because it can create a
hostile and unhealthy workplace for the
employees.
For this reason, the Congress of the
Philippines enacted the An:-Sexual Act of 1995
Declaring sexual harassment unlawful in the
employment, education or training environment,
and other purposes.
The State shall value the dignity of
every individual, enhance the
development of its human resources,
guarantee full respect for human rights,
and uphold the dignity of workers,
employees, applicants for employment,
students or those undergoing training,
instruction or education.
Towards this end, all forms of sexual
harassment in the employment,
education or training environment are
hereby declared unlawful.
SEXUAL ACT OF 1995
THE CIVIL RIGHT ACT OF 1964
OF
UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
This is where our law was perverted define
sexual
harassment as:
Unwelcome sexual advances, requests for
sexual favors, and other verbal or physical
conduct of a sexual nature constitutes sexual
harassment when submission to or rejection of
this conduct explicitly or implicitly affects an
individuals employment, unreasonably interferes
with an individuals work performance or creates
an intimidating, hostile or offensive work
environment.
REPUBLIC ACT NO. 7877
Defines sexual harassment as:
Employer, employee, manager, supervisor,
agent of the employer, teacher, instructor,
professor, coach, trainer or any other person
who, having authority, influence or moral
ascendancy over another in a work or training or
education environment demands, requests or
otherwise requires any sexual favor from the
other, regardless of whether the demand,
request or requirement for submission is
accepted by the object of said act.
WHY SEXUAL
HARASSMENT OCCURS?
Sexual harassment occurs due to power
struggle between men and women as a
response to a real or imagined loss of power or
as an expression of retaliation or a exing of the
new power.
This also happens because some
organizations and managers allow it to happen.
Historically, sexual harassment has always
occurred but there used to be no label for such
behavior.
The industrial revolution brought about changes in
the traditional function of men and women which greatly
increased gender specialization and formed a new kind of
workplace in the western world.
The responsibility of men and women became more
specialized.
In the past decades, things continue to change. More
and more women joined the workforce. They moved into
jobs that were traditionally held by men.
As a result of these changes, the balance is shibing.
Sexual harassment is one of the effect of this shib.
When harassment is commoved by a male against
a female, it may be a response to real or imagined
loss of power.
When commoved by a woman towards a man, it
may be an expression of retaliation or exing of the
new power.
Two Types of Sexual
Harassment
1. Quid Pro Quo Harassment
2. Harassment that creates a Hostile
Environment
This means this for that (something for
something)
This is defined as requiring a sexual favor or
interaction as a condition of employment or in exchange
for an employment benefit (such as promotion, transfer,
pay raise).
A manager uses his authority to grant pay increases
and promotions as a means to extort sexual favors from
an employee.
e.g., go to bed with me and you will get that
promotion
you want.
1. Quid Pro Quo Harassment
2. Harassment that creates a
Hostile Environment
In the hostile environment type of harassment,
abuses include verbal, physical and visual
conduct that creates an intimidating, offensive, or
hostile environment in the workplace that
interferes with work performance.
This type of harassment may be based on
race, religion, national origin, sex, age, marital
status, veteran status, sexual orientation, or
disability.
1. Unwanted touching, and pinching against a
person
2. Comments about your body, leering, wolf
whistling,
insults of a sexual nature, persistently pestering for
a date.
3. Displaying or circulating pornographic pictures
with
the intention of harassing someone / Posting of
explicitly sexual materials
4. Workplace blackmail- i.e. suggestion that
sexual
favors may further your career (or refusal may
hinder it)
5. Green jokes
6. Obscene levers
7. Sexual propositions
8. Suggestive looks
Some examples of a hostile
environment
1. The victim as well as the harasser may be
a woman or a
man. The victim does not have to be of the
opposite sex.
2. The harasser can be the victims
supervisor, an agent of the employer, a
supervisor in another area, a co-worker, or a
non-employee.
3. The victim does not have to be the person
harassed but could be anyone affected by the
offensive conduct.
4. The harassers conduct must be
unwelcome.
The profiles of the Victim and the
Harasser:
2. THE PROBLEM OF
JUST WAGE
Work and Compensation
Work
is said to be for the purpose of obtaining economic
gain for the laborer.
Most agreed that work is directed to the promotion
of
life.
The duty to preserve ones life implies the duty to
work and that each has a personal duty to take care
of himself and not to be a burden to other.
Being compensated for a work done or for services
rendered is the very essence of work.
Compensation
One is willing to work in exchange for remuneration
or
rewards he will receive from working.
Such remuneration may include both financial and
non--financial compensation.
It can be in the form of wages, shares on profits,
harvest or commercial goods, in-kind payments and
other remunerative fringe benefits.
The main objective of compensation is to create a
system of rewards that is equitable to the employer
and employee. Thus, the general concern is that
justice should be a substance of compensation.
A just wage is defined as the
remuneration which is enough to
support the wage-earner is
reasonable and frugal comfort.
The Catholic Church tells us, a just
wage is the legitimate fruit of labor.
The Question of Just Wage
Spread in various parts of the 1987
Philippine Constitution are specific
pronouncements and mandates on the
protection and promotion of the rights
of workers in the public and private
sectors, as indicated in lever g Sec 3
of Art. XIII.
That the workers are entitled to a
living wage
Philippine Constitution
The Wage Rationalization Act declared
the policy of the State to rationalize the
fixing of minimum wages and to promote
productivity-improvement and gain--
sharing scheme to ensure a decent
standard of living for the workers and
their families. The minimum wage rates
shall be adjusted in a fair and equitable
manner, considering existing regional
disparities in the cost of living and other
socio-economic factors.
Republic Act No. 6727
In our country, determination of wages
must also be adequate and just.
National Wage and Productivity
Commission (NWPC)
Regional Tripartite Wages and Productivity
Boards (RTWPB)
These determine the minimum wage for
Filipino workers
They handle the minimum wage rates of
the workers of each and every region of the
country
Government Agencies
Involved
Factors to consider in
Formulation of Fair Wages
1. External Market
Factor
These refers to the
supply and
demand for labor
and the so-called
economic
conditions and
underemployment.
2. Laws and
Regulations
Workers should be
paid in accordance
with laws and
regulations issued
by the government.
It requires that
employers pay at
least the minimum
wage.
Factors to consider in
Formulation of Fair Wages
3. Cost of Living
The cost of living
relates to basic
maintenance needs
and it must be
seriously considered
in formulation of
wages. A fair wage
should be sufficient
to meet the increase
in cost of living.
4. Prevailing
Industry Rate
Some claim that
paying workers the
average of what
other companies are
paying for the same
job result in a fair
wage. However not
all companies have a
minimum wage high
enough to maintain a
decent standard of
living.
Factors to consider in
Formulation of Fair Wages
5. Organizational
Factors
Assessment of what
type of industry the
organization
operates, the size of
the company, and
the organizations
profitability to justify
its ability to provide
fair wages to its
workers should be
considered.
6. Job Factor
The nature of the job
itself entails the
formulation of a just
wage. Duties,
responsibilities, and
the skills
requirements of the
job are probably the
most considerable
determinants of fair
wage.
Factors to consider in
Formulation of Fair Wages
7. Individual Performance
The trend is that individual
performance and productive effects
the denomination of wage/salary
increases.
Some Issues on Just Wage
The minimum wage mandated by the
government is not a guarantee of a just
and fair wage.
Organizations and businesses usually
conclude that they are legally and
morally right when they fulfill their mutual
agreement with the employees.
Geographical difference hinder the
formulation of a perfectly common
definition of fair wage. Some
communities have a higher cost of living
than others.
3. GIFT GIVING AND
BRIBERY
GIFT-GIVING
Is merely an act of extending
goodwill to an individual in an effort to
share something with particular
others.
Reasons why business usually
engage in gift-giving
1. To show appreciation for a favor
received
2. To effectively establish goodwill
with business partners.
3. To advertise
4. To compete effectively against
competitors
The following are the common
forms of Gift-Giving
Samples
Raffle coupons /
certificates
Rebates / cash refund
Padding expense
accounts
Premiums
Prizes
Patronage awards
(rewards)
Tie-up promotions
Allowance
Free goods
Tips
Is Gift-Giving Ethical or
Unethical?
Business gift of clients and business
associates can raise conflict of interest
problems, and knowing where to draw
the line, between what is right and
wrong, is not always easy.
The clear point is that those who cross
that line, intentionally or not, end up in
big trouble.
It is indeed difficult to determine the
morality of giving gift.
Factors in determining
Morality of Gift-Giving
1. Value of the gift
2. Purpose of the gift
3. Circumstances under which the gift
was given or received
4. Position between or relationship of the
giver and receiver
5. Acceptable business practice in the
industry
6. Company policy
7. Laws and Regulations
BRIBERY
It is defined as a practice of giving
renumeration for performance of an
act that is inconsistent with the work
contract or the nature of the work one
has been hired to perform.
It is intended to induce people inside
the business or other organizations to
make decisions that would be
justifiable according to normal
business or other criteria.
Example of bribery:
A motorist offered a certain amount of
money to a police officer in order not
to be issued a ticket for speeding.
A construction company shared
percentage of its income to a civil
servant in order to win a contract.
Bribery is obviously unethical
because
of the following reasons:
It is generally used as an instrument
to gain personal or corporate
advantage.
It corrupts the concept of justice and
equality
4.THE MORALITY OF
ADVERTISING
Advertising plays a very significant role in
marketing goods and services.
Without advertising, the consumers would
not be aware of the presence of diverse
products and services available in the
market.
Sometimes, even the mere presence of
advertising can sell a product due to
consumer perception that a heavily
advertised product is a product of good
value.
Some Issues in Advertising
These are those which either make a
false statement and therefore, lie, or
which represents the product without
making any statement.
This may not occur not only through
sentences but also through pictures,
individual words, or objects that can
deceive our eye and mind.
An example of this is one where pictures
from the box of the product do not look
the same as the contents of the product,
in this case, the picture is said to be
deceptive.
Deceptive Advertising
Use of Weasel Words
The use of weasel words is obey
complementary to ambiguity in
advertising.
Weasel words are used to avoid from a
direct or straightforward statement.
One example of a commonly used
weasel word is Help
Help means to aid or assist.
We are usually accustomed to ads that
contain phases like: help, ght, help
prevent, help stop
Like, can be, up to, as much as, are
used to imply what cannot be said.
Exaggeration
Consumers might also be misled
through exaggeration. This occurs
when advertisements tend to make
false claims of the benefits of the
goods or services which is actually
unsupported by valid evidences.
Psychological Appeals
There are some advertisements
that are directed at arousing human
emotional needs rather than reason.
Ads Directed at Children
Most advertisers have recognized that
advertising to children is effective and
eventually became a big business
recently.
Philippine Law on Advertising
CONSUMER ACT OF THE
PHILIPPINES
Article 108 of the act declares that
The State shall protect the consumer
from misleading advertisements and
fraudulent sale promotion practices.
The Department of Trade and
Industry is responsible for enforcing
the provisions of the act.
False, Deceptive and
Misleading Advertisement
Article 108 states that : it shall be
unlawful for any person to disseminate
or to cause the dissemination of any
false, deceptive or misleading
advertisement by Philippine mail or in
commerce by print, radio, television,
outdoor advertisement, or other
medium for the purpose of inducing or
which is likely to induce directly or
indirectly the purchase of consumer
product and services.
Special Requirements for Food, Drugs,
Cosmetics, Device or Hazardous
Substance
1. No claim in the advertisement should be
made that is not contained in the label or
approved by DOH
2. It is unlawful to advertise any food, drugs,
cosmetic, device or hazardous substance that is
false, misleading, or deceptive, or is likely to
create an erroneous impression regarding its
character, value, quantity, composition, merit, or
safety.
3. Where a standard has been prescribed for a
food, drugs, cosmetic, or device, no person shall
advertise any article or substance in a manner
that is likely to be mistaken for such product,
unless the product actually complies with the
prescribed standard.
Philippine Association of National
Advertisers (PANA)
In 1958, advertisers formed the
Philippine Association of National
Advertisers (PANA).Since then, the
PANA has been engaged in a
continuing campaign to regulate
abuses committed by untruthful
advertisers.
The PANA issued a Code of Ethics which
includes the following statement of general
principles:
Good advertising recognizes both its
economic and social responsibility to
help reduce distribution costs and to
serve the public interest.
Good advertising depends for its
success on public confidence. Hence,
it cannot permit those practices that
tend to impair this confidence.
5. OFFICE ROMANCE
Surveys says that somewhere from 25-33
percent of the employees at a given company
have had office romances once in their
careers.
About three-fourths of the people in the
survey believe that a romance at the office is
acceptable.
What is Office Romance?
It is defined as a relationship between
two people who are employed by the
same organization.
It is characterized by mutual attraction
between the parties and a desire for a
personal, romantic relationship.
Office romance is likely to happen as
long as men and women work
together.
Benefits of Office Romance
These benefits include friendship,
mutual support to each other at work,
and other personal experiences.
Employees involved in a love
relationship overcome rough times at
work because of mutual support and
inspiration.
Employees tend to view work as fun
even when pressures begin to pile up.
Romance becomes the reason to
keep their jobs.
Disadvantages of Office
Romance
Damaged professional reputations
Disturb co-workers
Changes in productivity
Dating the boss
Extramarital affairs
Interventions
Some companies want to restrict their employees to engage in office
romance. Others are in favor of the positive effects of office
romance, but may want to lessen the bad effects.
For example: some companies may allow relations between co-
workers with the same rank.
Legal / Ethical Considerations
When one or both involved parties are required to leave the
company, this risks legal encounters.
Policies regarding office romance need to be decided with vigilant
thought and prudence, in order to respect the rights of all members
of the organization.
Sexual Harassment
Sexual harassment may sometimes arise when a bad workplace
romance is terminated.
There are few reasons why this issue may exist.
One of the persons involve in a failed romance may seek vengeance,
may try to revive, or would want to remove the other person
involved.
There may be misinterpretation on the part of each party. One may
consider irting acceptable which may eventually lead to a romance,
while another may consider it oensive and therefore, a harassment.
Ethical Issues in Office Romance
6. THE PROBLEM OF FAIR
PRICING
In general, a fair price is one that man has not yet
resolved, though some factors are considered such as:
a) The cost of material
b) Operating and marketing expenses c)A reasonable
prot margin
-These factors constitute to set price fairly though it
is not enough to provide a precise answer on what a
fair price is.
- One should assess the factors on which the price is
based and the processes that determine it.
Ethical Issues in Fair Price
A. True cost of the product is concealed
B. Suggested retail price
C. Use of electronic scanners
D. Promotional pricing
E. Follow the leader pricing
F. Price gouging
G. Price xing
The Suki system of the Filipino
business compromises the fair price of a
regular customer from the new ones.
7. TRADE SECRETS AND
CORPORATE
DISCLOSURE
TRADE SECRET
A trade secret is the legal term for
confidential business information. That piece
of information allows the company to
compete effectively.
Examples of trade secret include customers
identities and preferences, vendors, product
pricing, marketing strategies, company
finances, manufacturing processes, and other
competitively valuable information.
These includes essentially any confidential
business information such as customer lists,
financial information, employee data,
production cost or sales data, and documents
memorializing important negotiations.
Trade Secret Act
The Trade Secret Act prevents wrongful
taking of confidential or secret
information.
Trade secret law prevents
misappropriation, wrongful taking, of
trade secret information. A wrongful
taking can occur in a variety of manners.
- For example, the taking of information
would be wrongful when the taking is a
breach of contract, breach of fiduciary
obligation, theb, and other illegal mavers.
CORPORATE DISCLOSURE
According to De George:
The moral basis for corporate disclosure rests primarily
on the following arguments:
1. Each person has the right to the information he needs
to enter into a transaction fairly.
The first basis speaks of information required for a
fair transaction.
A transaction is considered fair if the person has the
appropriate information needed for the transaction
2. Each person has the right to those actions of others
that will seriously and adversely affect him or her.
The second basis speaks of the moral responsibility of
the person.
As stated in the law, it is clear that a person is not
morally permived to harm others. But a person is
permived to do something that might cause others
harm.
8. PRODUCT
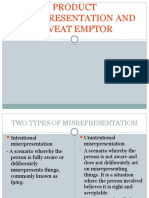
MISREPRESENTATION
Misrepresentation
Misrepresentation is observed when there is a
transformation of information to misinformation.
There are two types of misrepresenta:on:
1. Inten:onal Misrepresenta:on a scenario
whereby the person is fully aware or deliberately
misrepresents things, commonly known as lying.
2. Uninten:onal misrepresenta:on a scenario
whereby the person is not aware and does not
deliberately act on misrepresenting things. It is a
situation where the person involved believes that
it is the right and acceptable things to do. It is
commonly called as white lie.
Definition of Lying
Lying can be defined as the act of making
others believe something that they,
themselves, do not believe in.
It happens when somebody tries to
convince others with untrue statements.
St. Augustine defines lying as:
A speech that is contrary to what the person
is thinking with the intention to deceive.
A lie therefore, takes place when the persons
action are not in congruence with his
thoughts with the intention to deceive others.
Types of Lying
Use of ambiguous
terms
It is the act of
deliberately using
vague terms or
open-ended
statements that can
have several
meanings to mislead
people that one is
telling the truth.
Statement like: I was
at the office around
8:00 a.m.
Use of false
statements
It is the act of
making a statement
from which false
conclusions may be
drawn eventually
misleading others.
This is oben
observed in
advertising a product
to be the best--
seller brand.
Type of Lying
Through action
It is a type of lying
where the person
gets caught in the
act of wrongdoing.
Example: when
someone is caught
red-handed of
stealing and s:ll
denies the
accusation
Suppression of
correct information
It is an intentional or
unintentional act of
hiding the correct
information which
eventually mislead
others.
This act is
sometimes observed
in some crime
scenes wherein a
witness conceals he
truth for the sake of
his own security.
Business Practices Involving
Misrepresentation and Lying
Other Type of Misrepresentation
1. Direct misrepresentation
It is characterized by actively misrepresenting
something about the product or service. It gives the
business a bad name because deception and lying are
used in the process of selling the product to the
customers.
2. Indirect misrepresentation
It is characterized by omiging adverse information about
the product or service. It is passive deception and not
as obvious compared to direct misrepresentation. But it
s:ll contributes to the impression that businessmen are
liars and are out to make quick money.
Direct Misrepresentation
Deceptive packaging
Adulteration
Misbranding or mislabeling
Short weighing
Short-changing
Short measuring
Short numbering
Misleading advertisement
Indirect Misrepresentation
Caveat Emptor (let the buyer beware)
Deliberately withholding information
Business ignorance
Some examples of
misrepresentation
9. THE MORALITY OF LABOR
STRIKE
Strike Action or Strike
It describe collective action
undertaken by groups of workers in
the form of a refusal to perform work.
This is a tactic oben employed by
labor unions during collective
bargaining with an employer.
In an ordinary usage, the term strike
is oben used to describe all work
stoppages, regardless of the origin of
the dispute.
Workers go on strike for different
reasons:
For higher compensation
To improve the workplace
For shorter working days
To stop their wages from going down
For more benefits
Because they think their company has been
unfair
Conditions for employment include wages,
hours, sanitation, and safety, and several
other circumstances that affect the work of
the workers.
What are the Basic Rights of
Employees?
LABOR CODE OF THE
PHILIPPINES
This is an act to strengthen the
constitutional rights of workers to self--
organization and free collective
bargaining and to penalize unfair labor
practices.
TYPES OF STRIKE
Sit-down Strike
This is a strike in
which workers
show up to work,
but refuse to work.
It may include
preventing
transports from
entering or living in
an institution or a
company.
General Strike
This is a strike
affecting all areas
of a labor force
across many
industries, typically
throughout an
entire country or a
large section
thereof.
TYPES OF STRIKE
Sympathy Strike
This is a strike
initiated by workers
in one industry and
supported by
workers in a
separate but related
industry.
Jurisdictional
Strike
This refers to a
concerted refusal to
work undertaken by
a union to assert its
members right to
particular job
assignments and to
protest the
assignment of
disputed work to
members of another
union or to
unorganized
workers.
TYPES OF STRIKE
Economic Strike
This is based on a
demand for bever
wages or benefits
than the employer
wants to provide.
Wildcat Strike
This is against the
will of the
leadership of the
union, or without a
union.
Slow down Strike
This is a form of
work stoppage in
which employees
deliberately reduce
their individual
production.
Recognition
Strike
This is a kind of
strike forcing
employers to
recognize and deal
with them.
Is There a Right to Strike?
The right to strike is integral to the
process of wage bargaining in an
industrial economy.
Any employee has a right to withhold
his labor services from an employer if
he does not like the pay and benefits
the employer offers.
Workers who are willing to work for a
strike and the employer who wishes to
hire them have a legitimate right to do
so.
10. WHISTLE-BLOWING
Whistle-Blowing
This is the disclosure by an employee of
confidential information which relates to
some danger, fraud, or other illegal or
unethical conduct connected with the
workplace, be it of the employer or his
fellow employees.
Whistle-blower
This is someone in an organization who
witnesses behavior by members that is
either contrary to the mission of the
organization, or threatening to the public
interest, and who decides to speak out
publicly about it.
Whistle-blower
He is a person, employee, or officer of
any institution who believes that he has
been ordered to perform some act or he
obtained knowledge that the institution is
engaged in activities which:
a)Are believed to cause unnecessary
harm to third parties;
b)Are in violation of human rights;
c)Run counter to the defined purpose of
the institution or organization; and
d)Informs the public of this facts.
Types of Whistle-Blowing
Internal Whistle-
Blowing
This occurs within
the organization. It is
going over the head
of immediate
supervisors to inform
higher management
of the wrongdoing.
External Whistle-
Blowing
This occurs outside
the organization. It is
revealing illegal and
immoral activities
within the
organization to
outside individuals or
groups such as
media men, public
interest groups,
regulatory body, or
non-government
organization.
Kinds of External Whistle-blowing
A. Current those who blow the
whistle on present employers.
B. Alumni those who blow the whistle
on former employers.
C. Open whistle-blower discloses his
identity
D. Anonymous whistle-blower who
does not disclose his identity.
External Whistle-Blower
External whistle-blowers experience
each of the following forms of retaliation:
Lost their job or were forced to retire
Received negative job performance
evaluations
Had work more closely monitored by
supervisors
Were criticized or avoided by co--
workers
Were blacklisted from geging another
job in their field.
Internal Whistle-Blower
Internal whistle-blowing produces less
retaliation but also experience severe
emotional effects of their whistle blowing
activity:
Severe depression on anxiety
Feeling of isolation or powerless
Distrust of others
Declining physical health
Severe financial decline
Problems with family relations
11. MULTI-LEVEL MARKETING
(MLM) AND PYRAMIDING
Multi-Level Marketing
Multi-level marketing is a system of
selling in which one signs up other
people to assist him, and they in turn,
recruit others to help them.
It is a system of selling through many
levels of distributors, thus the word
multilevel Marketing
Each gets a percentage on the price of
the product being sold. This is also
known as direct selling companies.
Pyramiding
In the classic pyramid scheme, participants
avempt to make money solely by recruiting new
participants into the program.
The hallmark of these schemes is the promise of
sky-high returns in a short period of :me for
doing nothing other than handling over your
money and gegng others to do the same.
Pyramid schemes focus on the exchange of
money and recruitment.
At the heart of each pyramid is typically a
representation that new participants can recoup
their original investments by inducing others to
make the same investments.
Each person you bring to your pyramid is
promised future monetary rewards or bonuses
based on your advancement up the structure.
The fraudsters behind the pyramid scheme may go to
great lengths to make the program look like a
legitimate Multi-level marketing program.
But despite their claims to have legitimate products or
services to sell, these fraudsters simply use money coming in
from new recruits to pay o early stage investors.
But eventually the pyramid will collapse. At some point
the schemes get too big, the promoter cannot raise enough
money from new investors to pay earlier investors, and many
people except those at the very top of the pyramid, lose their
money. Many losers pay for a new winners. Pyramid operates on
recruitment.
It starts with one person that encourages six participants to
join. The 6 recruits will again get six to join making the number
involved 36 and will recruit and recruit will they reach 1296
participants in the pyramid.
At the 13th level they need to have 13 billion new recruits
which is impossible to sustain the pyramid. The pyramid will
collapse when no new participants can be recruited.
You might also like
- OIG ReportDocument18 pagesOIG ReportAnita WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Role of The State and Its Impact On Business OrganizationsDocument20 pagesRole of The State and Its Impact On Business OrganizationsBaby Joy Bautista100% (3)
- Moral Decision MakingDocument165 pagesMoral Decision MakingKira DomiogiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Taxation 101Document8 pagesFinal Exam Taxation 101Live LoveNo ratings yet
- Ethics Ah SungDocument5 pagesEthics Ah SungLau Pick SungNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Diagrams - LabitagDocument74 pagesOblicon Diagrams - LabitagDigoy Esguerra100% (3)
- Project On Organizational CultureDocument27 pagesProject On Organizational Cultureyatinastha76% (21)
- The Business Vision & Mission: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 12 Edition Fred DavidDocument58 pagesThe Business Vision & Mission: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 12 Edition Fred DavidLsc LondonNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper #8Document5 pagesReaction Paper #8Louelie Jean Alfornon100% (1)
- Good Gov 7-9 With Q&ADocument74 pagesGood Gov 7-9 With Q&AJoshua JunsayNo ratings yet
- Module Chapter 5 CSR 2021Document14 pagesModule Chapter 5 CSR 2021Rhod Jasper EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Ethics and BusinessDocument8 pagesEthics and BusinesspjNo ratings yet
- CSR Chapter 6 Explains ConceptsDocument30 pagesCSR Chapter 6 Explains ConceptsMaria Patrice MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1RoxaNe IkYheart CuNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Business Case StudyDocument11 pagesEthical Issues in Business Case Studyclarisse villegas100% (2)
- PPT-10 - Ethics in Consumer Protection and Community RelationsDocument31 pagesPPT-10 - Ethics in Consumer Protection and Community RelationsMuhammad Ali AdnanNo ratings yet
- 52170068Document11 pages52170068Joel Christian MascariñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Reno PhillipNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Introduction To Corporate GovernanceDocument6 pagesMODULE 1 Introduction To Corporate GovernanceMika100% (1)
- GGSRDocument14 pagesGGSRCarmela DimaalihanNo ratings yet
- Ethics 3.1 1Document38 pagesEthics 3.1 1Nicole Tonog AretañoNo ratings yet
- ETHICS and BUSINESS: Understanding the Importance of Morality in Corporate DecisionsDocument50 pagesETHICS and BUSINESS: Understanding the Importance of Morality in Corporate DecisionsLheapriaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document1 pageActivity 3Sheen CatayongNo ratings yet
- Case 7Document1 pageCase 7jona empalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 CreditDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Creditcharlyn mae generalNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Financial ManagementDocument8 pagesAn Overview of Financial ManagementCHARRYSAH TABAOSARESNo ratings yet
- Module 6.business EthicsDocument12 pagesModule 6.business EthicsShreeshaila P VijayapurNo ratings yet
- Ethics-Chap2 - Business Ethics and CSR ComparedDocument11 pagesEthics-Chap2 - Business Ethics and CSR ComparedCln CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Philippine Financial SystemDocument19 pagesTopic 1 Philippine Financial SystemJulie Anne DanteNo ratings yet
- Credit and CollectionDocument53 pagesCredit and CollectionApril CastilloNo ratings yet
- Good Governance & Social ResponsibilityDocument23 pagesGood Governance & Social ResponsibilityCristy RamboyongNo ratings yet
- MR Padua EssayDocument5 pagesMR Padua Essayjo anneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Role of Business ResearchDocument15 pagesChapter 1 The Role of Business ResearchAmanda Samaras100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Module 5 A Critical Survey of The Different Normative Ethical Theories Commonly Used in Business Decision MakingDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Module 5 A Critical Survey of The Different Normative Ethical Theories Commonly Used in Business Decision MakingAndy LaluNo ratings yet
- The Problem OF: Fair PricingDocument12 pagesThe Problem OF: Fair Pricinglena cpa100% (1)
- Objectives:: Business EthicsDocument5 pagesObjectives:: Business EthicsQuenie Rios Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- GoodgovpptDocument16 pagesGoodgovpptRuffa Garcia100% (1)
- ReflectionDocument1 pageReflectionashley100% (1)
- Gross Income Chapter SummaryDocument11 pagesGross Income Chapter SummaryharpyNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper #7Document5 pagesReaction Paper #7Louelie Jean AlfornonNo ratings yet
- HRM - Chapter 7Document15 pagesHRM - Chapter 7Caryl Joshua S. RoasaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Week 2 PE 004 Objectives and History in Basketball Darjay PachecoDocument5 pagesModule 1 Week 2 PE 004 Objectives and History in Basketball Darjay PachecoRocelle MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Assessment On The Practice of Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument12 pagesAssessment On The Practice of Corporate Social ResponsibilityJayson Tom Briva CapazNo ratings yet
- Video ReflectionDocument4 pagesVideo ReflectionXuan LimNo ratings yet
- Ethics and Business: Understanding Moral ReasoningDocument9 pagesEthics and Business: Understanding Moral ReasoningMao Chiongbian-Gorospe RoslindaNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Background of Business EthicsDocument6 pagesPhilosophical Background of Business EthicsDanica PadillaNo ratings yet
- Ojt Journal 1Document11 pagesOjt Journal 1Gerald F. SalasNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation Exclusions and Gross IncomeDocument6 pagesIncome Taxation Exclusions and Gross IncomeJane TuazonNo ratings yet
- ISO 9000 Quality Standards and Benchmarking ProcessesDocument3 pagesISO 9000 Quality Standards and Benchmarking ProcessesJomari Gingo SelibioNo ratings yet
- Admired Companies and Business Excellence ModelsDocument4 pagesAdmired Companies and Business Excellence ModelsDominador AspergaNo ratings yet
- MARKETING Module 1 For StudentDocument2 pagesMARKETING Module 1 For StudentJulianne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics in Philippine PerspectiveDocument18 pagesBusiness Ethics in Philippine PerspectiveANDELYN100% (1)
- Feb Case Snalysis 5Document2 pagesFeb Case Snalysis 5Kote GagnidzeNo ratings yet
- SRGGDocument31 pagesSRGGPinky LongalongNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Financial SystemDocument17 pagesThe Philippine Financial SystemCharisa SamsonNo ratings yet
- Foreign Banks: Ben Mathews T4 MbaDocument11 pagesForeign Banks: Ben Mathews T4 MbaBen MathewsNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyGavin Lynus Yuipco0% (1)
- Avoiding Conflicts of Interest in Hiring and SupervisionDocument6 pagesAvoiding Conflicts of Interest in Hiring and SupervisionAnish BatraNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics Module ExplainedDocument4 pagesBusiness Ethics Module ExplainedddddddaaaaeeeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Ethical Issues and Problems in Business and The Corporate WorldDocument37 pagesChapter 6 Ethical Issues and Problems in Business and The Corporate Worlddhanacruz2009100% (1)
- GGSR (Chapter 4A - Ethical Issues and Problems in Business and Corporate World)Document10 pagesGGSR (Chapter 4A - Ethical Issues and Problems in Business and Corporate World)Lysss Epssss100% (1)
- 5Document118 pages5Rina TruNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 (W)Document156 pagesLesson 4 (W)Niccolo G. ChiongbianNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 24010, October 22, 1925Document4 pagesG.R. No. 24010, October 22, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of the Philippines decision on payment of fines and costsDocument2 pagesSupreme Court of the Philippines decision on payment of fines and costsJTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 23133, August 20, 1925Document4 pagesG.R. No. 23133, August 20, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court Rules Lessee of Public Land Not Liable for TaxesDocument4 pagesSupreme Court Rules Lessee of Public Land Not Liable for TaxesJTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 23979, December 18, 1925Document6 pagesG.R. No. 23979, December 18, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court upholds woman's land title over estate in 1925 caseDocument5 pagesSupreme Court upholds woman's land title over estate in 1925 caseJTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 23948, November 19, 1925Document9 pagesG.R. No. 23948, November 19, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 23940, December 21, 1925Document4 pagesG.R. No. 23940, December 21, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 23977, July 22, 1925Document4 pagesG.R. No. 23977, July 22, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 23982, October 08, 1925Document8 pagesG.R. No. 23982, October 08, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of the Philippines rules on intestate estate partition disputeDocument6 pagesSupreme Court of the Philippines rules on intestate estate partition disputeJTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 23063, December 10, 1925Document7 pagesG.R. No. 23063, December 10, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of the Philippines rules on unpaid stock subscriptionsDocument4 pagesSupreme Court of the Philippines rules on unpaid stock subscriptionsJTupakNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court Philippines 1925 Land Exchange CaseDocument5 pagesSupreme Court Philippines 1925 Land Exchange CaseJTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 22824, January 24, 1925Document3 pagesG.R. No. 22824, January 24, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 22909, January 28, 1925Document5 pagesG.R. No. 22909, January 28, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 22825, February 14, 1925Document19 pagesG.R. No. 22825, February 14, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 22905, January 28, 1925Document7 pagesG.R. No. 22905, January 28, 1925JTupakNo ratings yet
- Adm. Case No. 101, March 27, 1968Document6 pagesAdm. Case No. 101, March 27, 1968JTupakNo ratings yet
- A.C. No. 217, November 27, 1968Document4 pagesA.C. No. 217, November 27, 1968JTupakNo ratings yet
- A. M. No. MTJ-00-1241, January 20, 2000Document10 pagesA. M. No. MTJ-00-1241, January 20, 2000JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 26, August 24, 1901Document4 pagesG.R. No. 26, August 24, 1901JTupakNo ratings yet
- A. C. No. 4980, December 15, 2000Document6 pagesA. C. No. 4980, December 15, 2000JTupakNo ratings yet
- Third Division (G.R. No. 137143, December 08, 2000: Panganiban, J.Document16 pagesThird Division (G.R. No. 137143, December 08, 2000: Panganiban, J.JTupakNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of the Philippines rules on short delivery claimDocument4 pagesSupreme Court of the Philippines rules on short delivery claimJTupakNo ratings yet
- A. M. No. P-98-1270. (Formerly OCA IPI No. 96-210-P), November 27, 2000Document5 pagesA. M. No. P-98-1270. (Formerly OCA IPI No. 96-210-P), November 27, 2000JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 25, December 07, 1901Document2 pagesG.R. No. 25, December 07, 1901JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 12, August 08, 1901Document3 pagesG.R. No. 12, August 08, 1901JTupakNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 6, November 14, 1901Document3 pagesG.R. No. 6, November 14, 1901JTupakNo ratings yet
- Infosys Whistleblower Policy SummaryDocument3 pagesInfosys Whistleblower Policy SummaryMaheshNo ratings yet
- mccg2021 1Document68 pagesmccg2021 1merNo ratings yet
- Ethics in EngineeringDocument10 pagesEthics in EngineeringSantanu BorahNo ratings yet
- Dealing With The Offshore EconomyDocument24 pagesDealing With The Offshore EconomyThe Atlantic CouncilNo ratings yet
- CSR report highlights sustainability leadership and innovationDocument80 pagesCSR report highlights sustainability leadership and innovationRayodcNo ratings yet
- 04 - Fraud Risk Management A Guide To GOOD PRACTICEDocument48 pages04 - Fraud Risk Management A Guide To GOOD PRACTICEEd Gonzales GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PPB 3233 Company Law Assignment 1 The Involvement of Company Employees in Fraudulent of CompaniesDocument13 pagesPPB 3233 Company Law Assignment 1 The Involvement of Company Employees in Fraudulent of CompaniesDashini VigneswaranNo ratings yet
- Exhibit A Keith E Miller MD Retaliation Against Dr. Shirley PigottDocument3 pagesExhibit A Keith E Miller MD Retaliation Against Dr. Shirley PigottShirley Pigott MDNo ratings yet
- R2117455Q Dissertation Recall Jirivengwa FinalDocument77 pagesR2117455Q Dissertation Recall Jirivengwa FinalRECALL JIRIVENGWANo ratings yet
- LTHEARDocument125 pagesLTHEARLaxmi BharuchaNo ratings yet
- Ethics, Social Responsibility, and SustainabilityDocument32 pagesEthics, Social Responsibility, and SustainabilityLeianneNo ratings yet
- Ethics of Whistleblowing and Speaking Truth to PowerDocument2 pagesEthics of Whistleblowing and Speaking Truth to PowerMARITEZZ MaloNo ratings yet
- Define the Role of Ethical EntrepreneursDocument9 pagesDefine the Role of Ethical EntrepreneursAlbert UmaliNo ratings yet
- Professional EthicsDocument28 pagesProfessional Ethicsprem kumarNo ratings yet
- Tata Code of ConductDocument6 pagesTata Code of ConductJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Whistle Blowing - Ethics Term PaperDocument16 pagesWhistle Blowing - Ethics Term PaperKheli-ann Clarke100% (2)
- Lankford Letter Re Ethics ComplaintDocument4 pagesLankford Letter Re Ethics ComplaintLaw&Crime100% (1)
- Future of HR 2019Document20 pagesFuture of HR 2019Mustafa KamalNo ratings yet
- Dreams Realised: APFT Berhad Annual Report 2018Document140 pagesDreams Realised: APFT Berhad Annual Report 2018Amira FarhidaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance in Public and Private SectorsDocument9 pagesCorporate Governance in Public and Private Sectorsjose mushambiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Corporate Social Responsibility Ethics and Sustainability PDFDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 3 Corporate Social Responsibility Ethics and Sustainability PDFAntora HoqueNo ratings yet
- Whistleblower Policy Nov2007Document2 pagesWhistleblower Policy Nov2007aspara411No ratings yet
- Deposition of Regent Doreen Stiles Poitevint - Post-OcrDocument25 pagesDeposition of Regent Doreen Stiles Poitevint - Post-OcrPIERS PLOWMAMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Summary Business Essentials Chapter 2 - Summary Business EssentialsDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - Summary Business Essentials Chapter 2 - Summary Business EssentialsAhmad MqdadNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Fraud in The Banking Industry PDFDocument79 pagesThe Impact of Fraud in The Banking Industry PDFCharisse LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in PhysicsDocument15 pagesEthical Issues in PhysicsASFDPNo ratings yet
- CBT TestDocument18 pagesCBT TestJulieBarrieNo ratings yet