Professional Documents
Culture Documents
P01 4e
Uploaded by
Eliecer Campos CárdenasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P01 4e
Uploaded by
Eliecer Campos CárdenasCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter One
Cost Management and Strategy:
An Overview
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Learning Objectives
Explain the use of cost management information for
each of the four functions of management and in
different types of organizations, with emphasis on
the strategic management function
Explain how the contemporary business
environment has influenced cost management
Explain contemporary management techniques and
how they have influenced cost management
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Learning Objectives
(continued)
Explain different competitive strategies that
companies can pursue
Describe the professional environment of the
management accountant, including professional
organizations and professional certifications
Understand the principles and rules of professional
ethics and explain how to apply them
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Introduction to Strategy
Success comes from developing and
implementing an effective strategy aided by
management accounting methods
Clear mission statement
Strategy is a roadmap to achieve a companys
mission
Management accountants can help a
company be successful
Key to success is having decision-relevant
information
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Competitive Strategies
A firm succeeds by implementing a set of
policies, procedures, and approaches to
business called strategy
Strategy must have a long-term focus and adapt
to the changing environment
Cost management information should be used to
develop and monitor strategic information
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Competitive Strategies (continued)
Aspect
Cost Leadership
Strategic
Target
Broad cross section of Focused cross section
the market
of the market
Basis of
competitive
advantage
Lowest cost in the
industry
Unique product or
service
Product line
Limited selection
Wide variety
Production
emphasis
Lowest possible cost Innovation in
and essential features differentiating products
Marketing
emphasis
Low price
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
Differentiation
Premium price and
innovative features
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Cost Management Information
Serves all management functions
Information a manager needs to manage
effectively
Financial and nonfinancial
Financial information alone shows a short-term focus
Developed under the direction of the controller for
the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) of the
organization
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Typical Organization Chart
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
Chief Financial
Officer (CFO)
Vice President
for Marketing
Vice President
for Operations
Controller
Treasurer
Chief Information
Officer (CIO)
Cost Management
Financial Systems
Financial Reporting
Other Reporting Obligations (e.g., tax)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
Cost Management vs.
Financial Reporting
Financial reporting
External users
Emphasis on accuracy and compliance
Cost management
Internal users
Emphasis on usefulness and timeliness, key
characteristics of decision-relevant information
Challenge for controller to reconcile these
potentially conflicting roles
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
10
Four Functions of
Management
Cost management information is
assembled to aid management in
the following functions:
Strategic management
Planning and decision-making
Management and operational control
Preparation of financial statements
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
11
Management Functions
Strategic management
Most important management function
Involves identifying and implementing goals and
action plans to maintain a competitive advantage
Monitoring of Critical Success Factors (CSFs) is
necessary
Critical to a firms success due to global competition
and rapidly changing markets
Strategic cost management information vs.
traditional cost management?
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
12
Management Functions (continued)
Planning and decision-making
Information is needed to support reoccurring
decisions such as scheduling production and pricing
Information is needed for short-run planning
(budgeting) and profit planning (Cost-Volume-Profit
analysis)
Management and operational control
Information is needed to identify inefficient
operations and reward effective management
practices
Preparation of financial statements
Information is needed to guarantee compliance with
regulations (GAAP) and regulatory reporting
requirements
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
13
Types of Organizations
Manufacturers
Manufacturers
Merchandisers
Merchandisers
Wholesalers
Wholesalers
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
Service
Service
firms
firms
Government
Governmentand
and
Not-for-profit
Not-for-profit
Retailers
Retailers
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
14
Changes in the Contemporary
Business Environment
1. Shift to a global business environment
Economic interdependence and increased
competition
2. New manufacturing technologies stemming
from the global business environment
Just-in-time (JIT) inventory methods and quality
control
Emphasis on speed-to-market (i.e., time-based
competition)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
15
Changes in the Contemporary
Business Environment (continued)
3. Importance of information technology
Increased use of the internet has reduced
processing time and facilitated information
exchange
4. Focus on the customer
Consumers expect functionality, quality and
customization
Shorter product life-cycles have intensified
competition
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
16
Changes in the Contemporary
Business Environment (continued)
5. Shifts in management organization
The focus has shifted from financial measures
and hierarchal command-and-control
organizations to nonfinancial measures and
flexible organizational structures
6. Social, political, and cultural considerations
Changes include a more diverse workforce, a
renewed sense of ethical responsibility, and
increased deregulation of business
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
17
How do these changes affect
management accounting?
The management accountants role:
Provide cost-management information at a
rigorous pace to keep up with the ever-changing
environment
The information provided should include as many
nonfinancial measures as possible a variety of
operating and financial measures
The reports should be applicable to crossfunctional teams and conducive with a flexible
management structure
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
18
Kaplans Phases for Developing Cost
Management Information Systems
Stage One
Cost-management systems are basic
transaction reporting systems
Stage Two
Cost-management systems focus on
external reportingdecision-usefulness
of cost-management data is limited
Stage Three Cost-management systems track key
operating data and relevant cost
information for decision-making
Stage Four
Strategically relevant cost-management
information is an integral part of the
system
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
19
Contemporary Management
Techniques
Benchmarking
Process by which a firm identifies its CSFs,
studies the best practices of other firms in
achieving these CSFs, and institutes change
based on the assessment results
Total Quality Management (TQM)
A technique by which management develops
policies and practices to ensure the firms
products and services exceed customers
expectations
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
20
Contemporary Management
Techniques (continued)
Business Process Improvement
Often associated with the previous two techniques,
this method involves managers and workers
committing to a program of continuous improvement
in quality and other CSFs
Activity-Based Costing and Management
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) improves the tracing of
costs to individual products and customers
Activity-Based Management (ABM) improves
operational and management control
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
21
Contemporary Management
Techniques (continued)
Reengineering
Process for creating a competitive advantage in
which the firm reorganizes its operating and
management functions, often resulting in modified,
combined, or eliminated jobs
The Theory of Constraints (TOC)
Helps firms improve cycle-time (i.e., the rate at
which raw materials can be converted to finished
products)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
22
Contemporary Management
Techniques (continued)
Mass Customization
Customers expect products and services to be
tailored to their unique needs creating the need for
smaller production runs
Target Costing
Target Cost = Market-determined price Desired
Profit
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
23
Contemporary Management
Techniques (continued)
Life-Cycle Costing
Costs should be monitored throughout a products
life cycle from research and development to sales
and service
Traditionally, only the costs incurred for
manufacturing, inspecting, packaging, and
warehousing were monitored
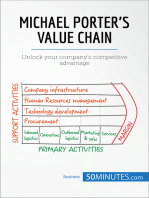
The Value Chain
An analysis tool used to identify the specific steps
required to provide a competitive product
Helps identify steps that can be eliminated or
outsourced
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
24
Contemporary Management
Techniques (continued)
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
An accounting report that addresses a firms
performance in four areas: financial, customer,
internal business processes, and innovation and
learning
Financial measures reflect only a partial, and
frequently only a short-term, measure of a firms
progress so the BSC incorporates both financial
and nonfinancial information
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
25
Professional Organizations
Organizations that provide guidelines and
regulations:
Internal Revenue Service (IRS), Federal Trade
Commission (FTC), Securities and Exchange
Commission (SEC), etc.
Organizations that promote professionalism
and competence:
Institute of Management Accountants (IMA),
Financial Executives Institute (FEI), and Institute
of Internal Auditors (IIA)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
26
Professional Certifications
There are three main certifications that are
relevant for management accountants:
Certified Management Accountant (CMA)
Certified Financial Manager (CFM)
Certified Public Accountant (CPA)
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
IMA Statement of Ethical
Professional Practice
27
Commitment to competence, integrity, confidentiality,
and credibility is necessary for the management
accountant to provide a useful service to management
When presented with an ethical issue that cannot be
resolved through your organizations established
policies, the IMA suggests a three step process:
Discuss the situation with a superior not involved in the issue
Clarify the issue through discussion with an IMA Ethics
Counselor or impartial advisor
Consult your own attorney as to your legal obligations and rights
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
28
Chapter Summary
Cost management information is used in all four of
the management functions and is important in the
pursuit of a firms mission and goals
The contemporary business environment expects
fast results and has influenced the role of the
management accountant
There were several contemporary management
techniques noted in this chapter that influence the
collection of cost management information
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
29
Chapter Summary (continued)
The two main competitive strategies are cost
leadership and differentiation
The management accountant looks to professional
organizations for guidelines and professional support
Professional certifications can be obtained in many
areas, but there are three main areas applicable to
management accountants
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
30
Chapter Summary (continued)
A commitment to professional ethics allows
management accountants to serve management
effectively
There is a three-step process provided by the IMA to
guide the management accountant through ethical
issues
Blocher,Stout,Cokins,Chen, Cost Management 4e
The McGraw-Hill Companies 2008
You might also like
- Chapter One: Cost Management and Strategy: An OverviewDocument23 pagesChapter One: Cost Management and Strategy: An OverviewIvankaNo ratings yet
- Cost Managment & StratDocument16 pagesCost Managment & Stratandit13No ratings yet
- The Changing Role of Managerial Accounting in A Dynamic Business EnvironmentDocument31 pagesThe Changing Role of Managerial Accounting in A Dynamic Business EnvironmentTeuku RizkyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten: Cost Planning For The Product Life Cycle: Target Costing, Theory of Constraints, and Strategic PricingDocument45 pagesChapter Ten: Cost Planning For The Product Life Cycle: Target Costing, Theory of Constraints, and Strategic PricingMade Ari HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Perspective: © Mcgraw-Hill EducationDocument12 pagesManagement Accounting Perspective: © Mcgraw-Hill Educationabeer alfalehNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Management Accounting Part 1: Scope and EvolutionDocument23 pagesEvolution of Management Accounting Part 1: Scope and EvolutionDabbie JoyNo ratings yet
- ACCY918 - Week1 - Introduciton and Cost Concepts - Lecture NoteDocument83 pagesACCY918 - Week1 - Introduciton and Cost Concepts - Lecture NoteNIRAJ SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Cost Management and StrategyDocument34 pagesChapter One: Cost Management and StrategySyafira Nida IsyaraniNo ratings yet
- Blocher 9e Chap001Document34 pagesBlocher 9e Chap001adamagha703No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Intro - CLC - HandoutDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Intro - CLC - HandoutMai ChiNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument13 pagesNotes4220019No ratings yet
- SCM Unit 1Document99 pagesSCM Unit 1Stevel PaciteNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument3 pagesOperations ManagementAshishAg91No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chapter 2Document51 pagesChapter 1 Chapter 221g40011No ratings yet
- C1 IntroDocument13 pagesC1 IntroNgọc Phương HoàngNo ratings yet
- Matrikulasi Ganjil 2023 2024Document204 pagesMatrikulasi Ganjil 2023 2024Beasiswa DSANo ratings yet
- Chap 001Document34 pagesChap 001Anonymous GDOULL9No ratings yet
- The Accountant's Role in The Organization: © 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedDocument16 pagesThe Accountant's Role in The Organization: © 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedWisnu WidodoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01finalDocument16 pagesChapter 01finalmohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Cost Management and StrategyDocument35 pagesChapter One: Cost Management and Strategymeliana100% (2)
- Ahead of The Curve: Forward-Looking Solutions For Tomorrow's Leading Asset Management FirmsDocument25 pagesAhead of The Curve: Forward-Looking Solutions For Tomorrow's Leading Asset Management FirmsAssetNo ratings yet
- BCF 403 Fundamentals of Production and Operations MGT - Module 1 PDFDocument29 pagesBCF 403 Fundamentals of Production and Operations MGT - Module 1 PDFNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- International Business Strategy FormulationDocument8 pagesInternational Business Strategy FormulationNumra ButtNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document4 pagesLesson 3Monique VillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2yared haftuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Cost Management StrategyDocument35 pagesChapter 1 - Cost Management StrategyHaniedar NadifaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting & Business EnvironmentDocument80 pagesManagerial Accounting & Business EnvironmentKhinwai HoNo ratings yet
- Garrison12ce PPT Ch01Document31 pagesGarrison12ce PPT Ch01Yatharth AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Dmba 201 - Production and Operations ManagementDocument12 pagesDmba 201 - Production and Operations ManagementPriya PriyaNo ratings yet
- MBA 122 Managerial Accounting Decision Making Lecture 1 Introduction Cost ClassificationDocument32 pagesMBA 122 Managerial Accounting Decision Making Lecture 1 Introduction Cost ClassificationfaisalhzNo ratings yet
- 74848bos60515 SPMDocument33 pages74848bos60515 SPMShubhamNo ratings yet
- Mba 507: Management Accounting: Revised Edition 2013 Published by Kenya Methodist University P.O. BOX 267 - 60200, MERUDocument73 pagesMba 507: Management Accounting: Revised Edition 2013 Published by Kenya Methodist University P.O. BOX 267 - 60200, MERUMarkmarie GaileNo ratings yet
- ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document25 pages©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Rey KardionoNo ratings yet
- Accounting & Control: Cost ManagementDocument25 pagesAccounting & Control: Cost ManagementMeriska100% (1)
- Role of MA in BusinessDocument42 pagesRole of MA in Businessdwi SuhartiniNo ratings yet
- NAAADocument3 pagesNAAAMonica AlauraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Management ACcounting EnvironmentDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Management ACcounting EnvironmentShedelyn PonponNo ratings yet
- Cost Management Handout Part 1Document14 pagesCost Management Handout Part 1Melwin jay mabanagNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting GuideDocument66 pagesManagerial Accounting Guidefarhan MomenNo ratings yet
- Kinney 8e - CH 19Document15 pagesKinney 8e - CH 19Ashik Uz ZamanNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Control System Design Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDocument5 pagesStrategy and Control System Design Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Basic Cost-Management ConceptsDocument19 pagesChapter Three: Basic Cost-Management ConceptsVebianti dewiNo ratings yet
- 04 Cost Drivers FinalDocument17 pages04 Cost Drivers FinalJerom EmmnualNo ratings yet
- The Accountant's Role in The Organization: © 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedDocument16 pagesThe Accountant's Role in The Organization: © 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedBlack TulipNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lecture 1aDocument20 pagesWeek 1 Lecture 1aDeer DeerNo ratings yet
- Accounting & Control: Cost ManagementDocument25 pagesAccounting & Control: Cost ManagementHAKUNA MATATANo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting & Control (Acecost) Chapter 1: Cost Accounting FundamentalsDocument8 pagesCost Accounting & Control (Acecost) Chapter 1: Cost Accounting FundamentalsXyne FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document22 pagesChap 002kamlakar gadegaonkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: Strategic Management: Planning For Long-Term SuccessDocument32 pagesChapter Seven: Strategic Management: Planning For Long-Term SuccessSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Operational StrategyDocument2 pagesOperational Strategyusme314No ratings yet
- Activity 2 Checa Margaux April M.Document5 pagesActivity 2 Checa Margaux April M.Ben TorejaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management Summer 2022 TOPIC 1: Overview of Cost Management and StrategyDocument4 pagesStrategic Cost Management Summer 2022 TOPIC 1: Overview of Cost Management and StrategyAang GrandeNo ratings yet
- MIS Strategic Planning ProcessDocument44 pagesMIS Strategic Planning ProcessHesbon Momanyi100% (1)
- Straco ReviewerDocument5 pagesStraco ReviewerKemberly JavaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis FrameworkDocument24 pagesStrategic Analysis Frameworkvignesh seenirajNo ratings yet
- What Is Operation ManagementDocument7 pagesWhat Is Operation Managementheysem100% (1)
- U1Document11 pagesU1Kaleab EnyewNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Chapter 1Document12 pagesCost Accounting Chapter 122100629No ratings yet
- Michael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageFrom EverandMichael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)From EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- SEMESTER-VIDocument15 pagesSEMESTER-VIshivam_2607No ratings yet
- DocsssDocument4 pagesDocsssAnne DesalNo ratings yet
- Pharma Society of GB Vs Boots Cash ChemistsDocument2 pagesPharma Society of GB Vs Boots Cash ChemistsRadhe MohanNo ratings yet
- Motion To DismissDocument4 pagesMotion To DismissYulo Vincent Bucayu Panuncio100% (1)
- Dispute Credit Report Inaccuracies FormDocument1 pageDispute Credit Report Inaccuracies FormJessica Ashley0% (1)
- Smart Mobs Blog Archive Habermas Blows Off Question About The Internet and The Public SphereDocument3 pagesSmart Mobs Blog Archive Habermas Blows Off Question About The Internet and The Public SpheremaikonchaiderNo ratings yet
- Mupila V Yu Wei (COMPIRCLK 222 of 2021) (2022) ZMIC 3 (02 March 2022)Document31 pagesMupila V Yu Wei (COMPIRCLK 222 of 2021) (2022) ZMIC 3 (02 March 2022)Angelina mwakamuiNo ratings yet
- RTO Question Bank EnglishDocument107 pagesRTO Question Bank EnglishRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Amgen Inc. v. F. Hoffmann-LaRoche LTD Et Al - Document No. 496Document3 pagesAmgen Inc. v. F. Hoffmann-LaRoche LTD Et Al - Document No. 496Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Identity Theft WebquestDocument2 pagesIdentity Theft Webquestapi-256439506No ratings yet
- Clem Amended ComplaintDocument26 pagesClem Amended ComplaintstprepsNo ratings yet
- STRONG vs. REPIDEDocument1 pageSTRONG vs. REPIDENicolo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Imam Al-Qurtubi's Tafsir of The Ayah: He Then Established Himself Over The Throne'Document3 pagesImam Al-Qurtubi's Tafsir of The Ayah: He Then Established Himself Over The Throne'takwaniaNo ratings yet
- Rahul IAS Notes on Code of Criminal ProcedureDocument310 pagesRahul IAS Notes on Code of Criminal Proceduresam king100% (1)
- Boie-Takeda vs. de La SernaDocument2 pagesBoie-Takeda vs. de La Sernazhengxiong100% (3)
- Pappu Kumar Yadaw's CAT Exam Admit CardDocument2 pagesPappu Kumar Yadaw's CAT Exam Admit Cardrajivr227No ratings yet
- Marraige and CompatabilityDocument3 pagesMarraige and CompatabilityRamesh Menon100% (1)
- Defensor Santiago v. ComelecDocument15 pagesDefensor Santiago v. ComelecRubierosse DongalloNo ratings yet
- Bwff1013 Foundations of Finance Quiz #3Document8 pagesBwff1013 Foundations of Finance Quiz #3tivaashiniNo ratings yet
- NELSON MANDELA Worksheet Video BIsDocument3 pagesNELSON MANDELA Worksheet Video BIsAngel Angeleri-priftis.No ratings yet
- Archipelago of Justice - Law in France's Early Modern EmpireDocument287 pagesArchipelago of Justice - Law in France's Early Modern EmpireaddeNo ratings yet
- Oliver Wyman Insurance Insights Edition 15 EnglishDocument7 pagesOliver Wyman Insurance Insights Edition 15 EnglishChiara CambriaNo ratings yet
- Ramadan Lantern Geo V2Document4 pagesRamadan Lantern Geo V2Little MuslimsNo ratings yet
- How May I Help You - Communication and Telephone Strategies - 1Document15 pagesHow May I Help You - Communication and Telephone Strategies - 1Gemma ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Extra Reading Comprehension Exercises (Unit 7, Page 80) Comprehension QuestionsDocument2 pagesExtra Reading Comprehension Exercises (Unit 7, Page 80) Comprehension Questionsroberto perezNo ratings yet
- 3000 Watt Power InverterDocument1 page3000 Watt Power InvertersimonNo ratings yet
- Reconstitution of a Partnership FirmDocument59 pagesReconstitution of a Partnership FirmKnowledge worldNo ratings yet
- Arthur Conan DoyleDocument13 pagesArthur Conan DoylealfonsougarteNo ratings yet
- WEC13 01 Que 20220111Document32 pagesWEC13 01 Que 20220111Mike JACKSONNo ratings yet
- 2011 Veterans' Hall of Fame Award RecipientsDocument46 pages2011 Veterans' Hall of Fame Award RecipientsNew York SenateNo ratings yet