Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Directfillinggold-Final Yr BDS
Uploaded by
Hanna AdnanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Directfillinggold-Final Yr BDS
Uploaded by
Hanna AdnanCopyright:
Available Formats
DIRECT FILLING GOLD
CONTENTS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
INTRODUCTION
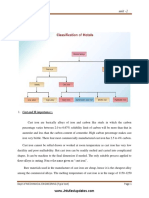
CLASSIFICATION
GOLD FOIL
ELECTROLYTIC PRECIPITATE
POWDER GOLD
MANIPULATION OF DIRECT FILLING GOLD
DESORBING OR DEGASSING
COMPACTION
ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES
INTRODUCTION
Pure gold can be used as an restorative
material.
Most noble metal, rarely tarnishes in oral
cavity
Cold welding property
Applications
1.
2.
3.
4.
Pits and small class I restorations
For repair of casting margins
For Class II and Class V restorations
Repair of cement vent holes in gold crowns
CLASSIFICATION
GOLD FOIL
Oldest
Manufacture:A cast ingot of 15 mm
thickness is beaten to a submicroscopic
thickness of 15 or 25 m
Supplied as:FIat square sheets of
varying thickness.
No. 4 wt. 4 grains (0.259 gram) 0.51 m
thick.
No. 3 wt. 3 grains (0.194 gram) 0.38 m
thick.
Preformed foils:
Ropes & cylinders available in preformed
shapes.
Made from No. 4 foil that has been
carbonized or corrugated
Platinized Foil
Pure platinum foil sandwiched b/w two
sheets of pure gold
Bonded by cladding process
Increases hardness
Available in No. 4 sheet form
Cohesive & Non-Cohesive Gold
Cohesive:
o
For cold welding gold should have a clean
surface
Gold attracts gases and any absorbed gas
film prevents cohesion of individual
increments of gold
Cohesive gold is supplied free of
contaminants
Non-Cohesive:
o
o
o
o
Gold is subjected to volatile agent such as
ammonia, which is absorbed on surface
Acts as a protective film
Volatile film readily removed by heating
Rarely used nowadays
ELECTROLYTIC PRECIPITATE
Crystalline gold powder is formed by electrolytic
precipitation. Powder is formed into shapes by
sintering(heat fusion).
Available as: mat, mat foil & alloyed
Mat gold:
Crystalline
Formed in strips
Easy to build up the internal bulk, more easily compacted &
adapted
Results in pitted external surface, so covered with a veneer of
foil gold
Mat foil:
Sandwich of electrolytic precipitated gold powder b/w sheets
of No.3 gold foil
Done to eliminate the need to veneer the
restoration with a layer of foil
No longer marketed
Alloyed Electrolytic Precipitate:
Newest form is Electraloy RV
Alloy of gold & calcium (0.1 to 0.5% by wt)
Calcium produce stronger restoration by
dispersion strengthening
Alloy sandwiched b/w two layers of gold
POWDER GOLD
Gold powder is enclosed in a No.3 gold foil
Manufacture:
Fine powder is formed by chemical precipitation or atomizing the
metal
Pellets mixed with soft wax, burned off later & wrapped in gold foil
Available as:
Foil acts as an effective container and matrix for the powdered
metal
Powdered gold pellet increases cohesion & reduces time required
for placing it, because each pellet contain more metal by volume
tan same sized pellet of gold foil
Powdered gold pellets have cylindrical or irregular shape &
diameter of 1 2mm
Ratio of gold foil to powder varies from 1 to 3 for small pellets to 1
to 9 for largest
MANIPULATION OF DIRECT FILLING
GOLD
There are two process involved
1.
2.
Degassing
Compaction
DESORBING OR DEGASSING
During storage & packing of cohesive gold,
they absorb gasses from atmosphere
Prevents it from fusing
Removed by heating- DEGASSING
Heating done in two ways
1.
2.
In bulk on a tray, by gas-flame or electricity
Piece by piece, in a well adjusted alcohol flame
Totally dry cavity needed to allow complete
cohesion
COMPACTION
The gold may be compacted by
1.
2.
3.
Hand mallet
Pneumatic vibratory condenser
Electrically driven condensers
PROPERTIES OF COMPACTED GOLD
STRENGTH:Greatest strength-most dense area
Weakest part- porous area
In DFG failure occurs from incomplete cohesion, thus
transverse strength is a measure of cohesion
HARDNESS
Indicates overall quality
Indicates presence of porosity
DENSITY
Density of pure gold is 19.3gm/cm
DFG density less than pure gold because it is not possible to
eliminate voids completely during compaction
EFFECT OF VOIDS
Amount of voids estimated by apparent density of compacted
gold
Voids on surface, increase susceptibility to corrosion and
deposition of plaque
Voids at the restoration-tooth interface cause gross leakage
and secondary caries development
TARNISH & CORROSION
Resistance to tarnish and corrosion is good if compacted well
BIOCOMPATIBILITY
Pulpal response is minimal if compacted well
This procedure causes a certain amount of trauma to the tooth
and supporting structures
Mechanical condensor causes less trauma than the manual
technique
ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES
Tarnish and corrosion resistant
Good mechanical properties
Good biocompatibility
DISADVANTAGES
Poor esthetics
High coefficient of thermal expansion
Manipulation is difficult
THANK YOU
You might also like
- BY, Smijal GMDocument17 pagesBY, Smijal GMMohamed FaizalNo ratings yet
- 6 Direct Filling GoldDocument100 pages6 Direct Filling GoldShresthaNo ratings yet
- DFGDocument62 pagesDFGSatavisha MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Direct Filling GoldDocument21 pagesDirect Filling GoldHariprasad LNo ratings yet
- Direct Filling GoldDocument22 pagesDirect Filling GoldMirza Abdul rahman baigNo ratings yet
- Direct Filling GoldDocument49 pagesDirect Filling Goldjtsnthkrl0% (2)
- Direct Filling Gold 30 04 2020Document27 pagesDirect Filling Gold 30 04 2020Sonam RawatNo ratings yet
- Direct Filling GoldDocument66 pagesDirect Filling GoldVimalKumarNo ratings yet
- Dental Casting and Soldering AlloysDocument40 pagesDental Casting and Soldering AlloysMella Bella WilsonNo ratings yet
- Hard Gold Plating Vs Soft Gold Plating - Which Is Right For My Application?Document5 pagesHard Gold Plating Vs Soft Gold Plating - Which Is Right For My Application?MRousstiaNo ratings yet
- 19castingalloys 140604163225 Phpapp02Document30 pages19castingalloys 140604163225 Phpapp02Mohamed NagibNo ratings yet
- Direct Filling GoldDocument29 pagesDirect Filling GoldanshumankhaitanNo ratings yet
- Soft and Hard Soldering +brazingDocument28 pagesSoft and Hard Soldering +brazingJoseph Magbanua Dato-on67% (3)
- Seminar HeraeusDocument91 pagesSeminar HeraeusArif Tirto AjiNo ratings yet
- Metals 2023 2024Document36 pagesMetals 2023 2024Joshua TupasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers: Metallurgy of TungstenDocument22 pagesChemistry For Engineers: Metallurgy of TungstenJustine joy cruzNo ratings yet
- N CGLDocument70 pagesN CGLjoshibecNo ratings yet
- Gold NewDocument23 pagesGold Newjust nomiNo ratings yet
- Green Book SolutionDocument44 pagesGreen Book SolutionCaleb RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Manufactured substances in industryDocument9 pagesManufactured substances in industryeyeda2000No ratings yet
- DFG - Total ClassDocument37 pagesDFG - Total ClassSiva RamNo ratings yet
- Gold Plating: Alan BlairDocument2 pagesGold Plating: Alan BlairHiden HidenNo ratings yet
- Annealing PDFDocument5 pagesAnnealing PDFKamran ShakeelNo ratings yet
- B Mason NotesDocument5 pagesB Mason Notesjsmithy456No ratings yet
- Non-Ferrous MetalsDocument26 pagesNon-Ferrous MetalsNicole May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Non-Ferrous& AssignmentDocument9 pagesNon-Ferrous& AssignmentOwen LunaticNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron & Steels ClassificationDocument28 pagesCast Iron & Steels ClassificationMadheswaran DharmapuriNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel AOD Operation and Slag Optimisation PDFDocument41 pagesStainless Steel AOD Operation and Slag Optimisation PDFPrakash MishraNo ratings yet
- Name: Safiuddin Bin Johari Class: 4 Bestari Tittle: The Process of Pewter Production in IndustryDocument18 pagesName: Safiuddin Bin Johari Class: 4 Bestari Tittle: The Process of Pewter Production in IndustrySafiuddin JohariNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Metallurgy-Manufacturing Process, Grades & Role of Alloying ElementsDocument35 pagesStainless Steel Metallurgy-Manufacturing Process, Grades & Role of Alloying ElementsLalit MohanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 and 4 NON-FERROUS MATERIALSDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 3 and 4 NON-FERROUS MATERIALSJibril JundiNo ratings yet
- CERAMICSDocument41 pagesCERAMICSramandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Solder Joint Embrittlement Mechanisms Solutions Standards IpcDocument17 pagesSolder Joint Embrittlement Mechanisms Solutions Standards IpcRobert MartosNo ratings yet
- MMAW - Smaw FillersDocument5 pagesMMAW - Smaw FillersrkqaqcweldingNo ratings yet
- Metallic Fibres GuideDocument28 pagesMetallic Fibres Guidemahe_ft100% (2)
- What is cast iron? Key properties and typesDocument27 pagesWhat is cast iron? Key properties and typesSanthoshsharma Devaraju100% (1)
- Welding, Soldering & Brazing Techniques for Dental ApplicationsDocument23 pagesWelding, Soldering & Brazing Techniques for Dental ApplicationsArchanaNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel AOD Operation and Slag OptimisationDocument41 pagesStainless Steel AOD Operation and Slag OptimisationRamiz Shaikh100% (1)
- How To Distinguish Carbon and Stainless Steel ?Document15 pagesHow To Distinguish Carbon and Stainless Steel ?getrajaNo ratings yet
- Zirconium Alloys Rev1 1Document19 pagesZirconium Alloys Rev1 1Christian AganoNo ratings yet
- S.G. Iron : MouldingDocument11 pagesS.G. Iron : MouldingsureshbabuamalaNo ratings yet
- Comp ProcDocument2 pagesComp ProcJuned VhoraNo ratings yet
- Dental AmalgamDocument3 pagesDental AmalgammanreenajitNo ratings yet
- Food Packaging Technology Unit 2 Part CDocument20 pagesFood Packaging Technology Unit 2 Part CAkash DuttaNo ratings yet
- Food Packaging: Unit 1 - MetalsDocument22 pagesFood Packaging: Unit 1 - MetalsKumkum CrNo ratings yet
- Soldering & WeldingDocument82 pagesSoldering & WeldingRachita Arora100% (1)
- Cast iron component failure investigationDocument4 pagesCast iron component failure investigationdelta lab sangliNo ratings yet
- New Galvanizing TechnologyDocument4 pagesNew Galvanizing Technologywmaddoxmec100% (1)
- Engineering Material LEC#2Document42 pagesEngineering Material LEC#2Sharjeel FaisalNo ratings yet
- Preview BinDocument38 pagesPreview BinNoob SssNo ratings yet
- FERROUS MATERIAL PROPERTIESDocument20 pagesFERROUS MATERIAL PROPERTIESLorenzoNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument34 pagesProjectSTAR PRINTINGNo ratings yet
- 50 Casting DefectsDocument49 pages50 Casting DefectsmohammadNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron Welding GuideDocument31 pagesCast Iron Welding Guideharoub_nasNo ratings yet
- Coating General PDFDocument15 pagesCoating General PDFOscar SotomayorNo ratings yet
- @@@dental AmalgamDocument120 pages@@@dental AmalgamUsama Mohamed100% (2)
- Casting & Welding TechnologyDocument8 pagesCasting & Welding TechnologySarabjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Casting Alloys: V.NivedhaDocument84 pagesCasting Alloys: V.NivedhaApurva DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Magical Metal Clay: Amazingly Simple No-Kiln Techniques For Making Beautiful AccessoriesFrom EverandMagical Metal Clay: Amazingly Simple No-Kiln Techniques For Making Beautiful AccessoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- ToLiss AirbusA321 V1.0.3 TutorialDocument103 pagesToLiss AirbusA321 V1.0.3 TutorialMarc CerveraNo ratings yet
- TLE-MAJOR-TEST-SET-010-Basic-electricity-1Document9 pagesTLE-MAJOR-TEST-SET-010-Basic-electricity-1edsonlligananNo ratings yet
- QS. EXAM Math 9th GradeDocument4 pagesQS. EXAM Math 9th Gradetikafebriani52No ratings yet
- Closed Loop Speed Control of a DC Motor Lab ManualDocument9 pagesClosed Loop Speed Control of a DC Motor Lab ManualnatashaNo ratings yet
- Dragonox-1098: Pine Chemicals Polymer Additives Petrochemicals ProductsDocument2 pagesDragonox-1098: Pine Chemicals Polymer Additives Petrochemicals ProductsXuân Giang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Tools and MaterialsDocument71 pagesTools and MaterialsMahardikaNo ratings yet
- Mdu 1Document3 pagesMdu 1Gaurang Agrawal0% (1)
- Chapter 3 Developing The Whole PersonDocument15 pagesChapter 3 Developing The Whole PersonRocel DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Deer and The CrocodilesDocument4 pagesThe Deer and The CrocodilesM Rifky FauzanNo ratings yet
- Piaggio Fly 125 I.E - 150 I.E Leader MY 2011 (EN)Document231 pagesPiaggio Fly 125 I.E - 150 I.E Leader MY 2011 (EN)ManuallesNo ratings yet
- Context CluesDocument4 pagesContext CluesSherelyn BaidoNo ratings yet
- Sas Lesson - MathDocument6 pagesSas Lesson - Mathapi-280008473No ratings yet
- AGBT05-18 Guide To Bridge Technology Part 5 Structural DraftingDocument73 pagesAGBT05-18 Guide To Bridge Technology Part 5 Structural DraftingyasNo ratings yet
- A House of Many Mansions: The History of Lebanon ReconsideredDocument256 pagesA House of Many Mansions: The History of Lebanon ReconsideredAnıl Koca100% (2)
- Intel® Core™2 Quad Processor Q9550 (12M Cache, 2.83 GHZ, 1333 MHZ FSB) SpecificationsDocument5 pagesIntel® Core™2 Quad Processor Q9550 (12M Cache, 2.83 GHZ, 1333 MHZ FSB) SpecificationsRobert FarkasNo ratings yet
- Cooling Fan Motor (Spin-on Element) (Square Solenoid Coil) Parts ListDocument2 pagesCooling Fan Motor (Spin-on Element) (Square Solenoid Coil) Parts ListEdgar SanchezNo ratings yet
- Advancing Social Justice, Promoting Decent WorkDocument29 pagesAdvancing Social Justice, Promoting Decent WorkalnaturamilkaNo ratings yet
- PSC&O Lab4Document3 pagesPSC&O Lab4Hafeez AliNo ratings yet
- Action Paper g2 Final OutputDocument67 pagesAction Paper g2 Final Outputjay diazNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - ProsperDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 - ProsperMuhammad Amirullah SanadiNo ratings yet
- Frisco 2023 DigitalDocument52 pagesFrisco 2023 DigitalEric MillerNo ratings yet
- 21 Day Fat Loss Nutrition Program Book PDFDocument89 pages21 Day Fat Loss Nutrition Program Book PDFJohnDNo ratings yet
- CV - Sanjana DhaidwalDocument1 pageCV - Sanjana DhaidwalPayal KathiawadiNo ratings yet
- Request for Learner Data CorrectionDocument4 pagesRequest for Learner Data CorrectionChaii Madlangsakay TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Bcoc 138Document2 pagesBcoc 138Suraj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Articulator Selection For Restorative DentistryDocument9 pagesArticulator Selection For Restorative DentistryAayushi VaidyaNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Tourism Master Plan 1991-2010Document7 pagesThe Philippine Tourism Master Plan 1991-2010Zcephra MalsiNo ratings yet
- CPSA Sales Institute Key Competencies in SalesDocument1 pageCPSA Sales Institute Key Competencies in Salesmiguel8blancoNo ratings yet
- 06.07 Review and Critical ThinkingDocument2 pages06.07 Review and Critical ThinkingmarielaNo ratings yet
- Anticharm 2Document15 pagesAnticharm 2api-3697331100% (1)