Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gender in World Politics
Uploaded by
Michelle MuirCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gender in World Politics
Uploaded by
Michelle MuirCopyright:
Available Formats
Gender in World Politics
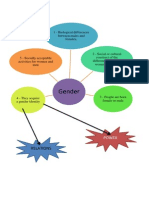
How do women participate in IR?
Always had a role BUT in non-gov settings i.e social movements rather than
policy-making
Womens voices rarely heard in leadership settings, yet they are affected by
leadership decisions
i.e: women and children make up most of the civilian casualties
: women are the majority of the poorest population
What do feminists mean by gender?
Everyday use gender = biological sex
Feminist view gender = set of socially and culturally constructed
characteristics that vary/time&space
Characteristics such as power, autonomy, rationality associated with
masculinity => perceived to have a more positive value by both men AND
women as well as most valued in states foreign policies
Female and male characteristics are mutually exclusive => if we give men
power, we give women weakness
These are social constructs as powerful, influential women often act like real
men
Gender becomes a mechanism for the unequal distribution of social benefits
and costs => we need to make unequal gender structures visible to remove
them
Gender in Global Politics
Women are disproportionately situated in low-paid occupations far from power WHY?
Liberal Feminism: observe how womens presence (or lack of) in practices of global
politics affect international policy-making removing legal obstacles to women would
achieve equality
Feminist Critical Theory: gender depends on the relations between men and women
changes in the meaning of gender have different effects on policies
Feminist Social Constructivism: study how gender influences global politics and politics
influence gender; regulating home-based work is important for feminists -> analysed
how home workers (usually women) were treated poorly as they were not considered as
important
Feminist Poststructuralism: concerned with the knowledge power relationship (those
who construct meaning and create knowledge gain power through it); men historically
seen as the knowers -> gained power; gendered messages are encoded in society
regardless of the intentions of the authors
Post-colonial Feminism: relations of domination-subordination still exist; womens
subordinations must be addressed within their own cultural context rather than
universal understanding
Gendering Security
men fight wars to protect women and children yet 90% of casualties are civilian,
mostly women and children- challenge the protection myth
Women particularly vulnerable in states of conflict systematic rape and
prostitution i.e Bosnia: rape= ethnic cleansing through forced pregnancies
Military training degrades all that is feminine; young men fight wars to protect the
helpless women and children, so they have to be strong enemy often given
feminine characteristics: weak, coward
Now there are more women in military tension with embedded view with what it
means to be a warrior often negative effect on combat readiness should women
fight in mens wars?
In conflict, both women and men look towards strong figures often associated with
men might explain why there are few women in military / top executive positions
Gender in the Economy
Women disproportionately located at the bottom of the socio-economic scale
in ALL societies earn 2/3 of a mans wage
Association of women with domestic roles housewife has become
institutionalised => now seen as almost natural reduces autonomy and
economic security
Women choose low-paid, caring positions not just due to rationality but also
expectations as mothers and caregivers that they are socialised in from a
young age -> often seen as supplemental wage earners to the male head
When women do work for wages, this undermines the legitimacy of male
domination that occurs due to the mens traditional head of family view
How are we working to change this?
UN Decade for Women
Development Alternatives with Women for a New Era (DAWN)
Pressure from womens groups to disaggregate data by sex
Adoption of the Gender Development Index
Gender Mainstream adoption requires organisations to evaluate the
gendered effects of all aspects of their institutional decision-making
You might also like
- Gender, Power, and Non-Governance: Is Female to Male as NGO Is to State?From EverandGender, Power, and Non-Governance: Is Female to Male as NGO Is to State?Andria D. TimmerNo ratings yet
- Obstacles To Women's Participation in ParliamentDocument19 pagesObstacles To Women's Participation in ParliamentDibakar Das100% (1)
- Gender SocializationDocument25 pagesGender SocializationAshley JoyceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnthropologyDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Anthropologymichael olajideNo ratings yet
- Would You Describe The Enlish Language As SexistDocument3 pagesWould You Describe The Enlish Language As SexistAdade GeorgeNo ratings yet
- The Bantu Education in South AfricaDocument7 pagesThe Bantu Education in South Africamisterario misterarioNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Growth and Gandhi's Swaraj ComparedDocument18 pagesInclusive Growth and Gandhi's Swaraj ComparedRubina PradhanNo ratings yet
- Women and Men: Hand in Hand Against ViolenceDocument168 pagesWomen and Men: Hand in Hand Against ViolenceOxfamNo ratings yet
- FeminismDocument6 pagesFeminismapi-337161139No ratings yet
- Jyothi Venkata 1Document12 pagesJyothi Venkata 1Hanuma NaikNo ratings yet
- Gender Inequality & Women Empowerment.Document20 pagesGender Inequality & Women Empowerment.Saba PervezNo ratings yet
- Gender Studies Lec 1Document26 pagesGender Studies Lec 1MujeebNo ratings yet
- Impact of Globalisation Social and Cultural Values in IndiaDocument37 pagesImpact of Globalisation Social and Cultural Values in IndiaRavikiranNo ratings yet
- NCF 2005 Chapter SummaryDocument6 pagesNCF 2005 Chapter SummaryRadhaSharma100% (1)
- The Social Protection Indicator for Asia: Assessing ProgressFrom EverandThe Social Protection Indicator for Asia: Assessing ProgressNo ratings yet
- Women in Conflict and Peace PDFDocument170 pagesWomen in Conflict and Peace PDFShabana AqilNo ratings yet
- Nature of SociologyDocument7 pagesNature of SociologyNÖrilly DixsyNo ratings yet
- Gender DiscriminationDocument14 pagesGender DiscriminationRaghu YadavNo ratings yet
- Social Change and EvolutionDocument15 pagesSocial Change and Evolutioncooooool1927100% (2)
- Women Empowerment: Remyachandran NSS Training College PandalamDocument6 pagesWomen Empowerment: Remyachandran NSS Training College Pandalamremya chandranNo ratings yet
- IntersectionalityDocument10 pagesIntersectionalityHuckleberry BeeNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Marxism Theory of Int'l RelationsDocument13 pagesGroup 3 - Marxism Theory of Int'l RelationsPowers Arthur SamuelNo ratings yet
- Women Empowerment Key to Bangladesh EconomyDocument13 pagesWomen Empowerment Key to Bangladesh EconomyLasania FerdouesNo ratings yet
- Aman Rao ProjectDocument10 pagesAman Rao ProjectAman RaoNo ratings yet
- Gender Based Violence in India - A Never-ending IssueDocument10 pagesGender Based Violence in India - A Never-ending Issuerev_allanNo ratings yet
- Sharing Knowledge, Transforming Societies: The Norhed Programme 2013-2020From EverandSharing Knowledge, Transforming Societies: The Norhed Programme 2013-2020No ratings yet
- MA Sociology Paper IIDocument73 pagesMA Sociology Paper IInaveengargnsNo ratings yet
- Social Theories PDFDocument10 pagesSocial Theories PDFMaryam QureshiNo ratings yet
- Rowlands, Empowerment Examined 1995Document7 pagesRowlands, Empowerment Examined 1995api-3767844No ratings yet
- The Role of Gender Studies PDFDocument14 pagesThe Role of Gender Studies PDFNadeem SheikhNo ratings yet
- The Role of Women and Youth in National Development: Perdana Discourse Series, #10From EverandThe Role of Women and Youth in National Development: Perdana Discourse Series, #10No ratings yet
- Dependency Theory 1 PDFDocument19 pagesDependency Theory 1 PDFTawny ClaireNo ratings yet
- Cross Cultural UnderstandingDocument12 pagesCross Cultural UnderstandingLily SinagaNo ratings yet
- Democracy As A Universal ValueDocument3 pagesDemocracy As A Universal ValueJay Pow100% (1)
- Men, Gender and MasculinityDocument1 pageMen, Gender and MasculinitynuribuNo ratings yet
- Are There Feminist Research Methods Mona KrookDocument20 pagesAre There Feminist Research Methods Mona KrookFabiana SeveriNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NUMBER 1: Basic Concepts of Public Policies & TheoriesDocument11 pagesLECTURE NUMBER 1: Basic Concepts of Public Policies & Theoriessaad aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 STRATIFICATIONDocument29 pagesChapter 5 STRATIFICATIONBholaNo ratings yet
- Women and Gender PDFDocument140 pagesWomen and Gender PDFAnonymous UE1TSLNo ratings yet
- Colonial Mode of ProductionDocument4 pagesColonial Mode of ProductioninnakkNo ratings yet
- Feminism: A Guide to Its Main Types and TheoriesDocument7 pagesFeminism: A Guide to Its Main Types and TheoriesagamNo ratings yet
- SexismDocument40 pagesSexismArpit PradhanNo ratings yet
- Political SC Sem 3Document20 pagesPolitical SC Sem 3Ayush ShivhareNo ratings yet
- Social Change and Education: Haqiqat Ali Nift-Hyderabad 9/20/2012Document15 pagesSocial Change and Education: Haqiqat Ali Nift-Hyderabad 9/20/2012Haqiqat Ali100% (1)
- Gender Roles in Media An Annotated BibliographyDocument6 pagesGender Roles in Media An Annotated Bibliographyapi-291753495No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document20 pagesLecture 1Misha WaseemNo ratings yet
- Gunnar Myrdal's Concept of Underdevelopment and CausesDocument17 pagesGunnar Myrdal's Concept of Underdevelopment and CausesmarielNo ratings yet
- Socialisation Sheet RevisionDocument1 pageSocialisation Sheet Revisionapi-235423294No ratings yet
- FunctionalistDocument1 pageFunctionalistAnonymousNo ratings yet
- 26 Jean Jacques Rousseau (1712-1770 A.D.) : Scanned With CamscannerDocument20 pages26 Jean Jacques Rousseau (1712-1770 A.D.) : Scanned With CamscannerShaman KingNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Education Commissions and Policies Since IndependenceDocument24 pagesUnit 5 Education Commissions and Policies Since IndependenceDoris ChhangteNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Participation of Women in PoliticsDocument13 pagesAssignment On Participation of Women in Politicsসুমন আহমেদ100% (2)
- Revolution and Enlightenment (Political Ideas ADocument13 pagesRevolution and Enlightenment (Political Ideas ADan HarringtonNo ratings yet
- Sarah LongweDocument13 pagesSarah Longwedememorir100% (3)
- Gender and Social Policy in A Global Context: Shahra Razavi and Shireen HassimDocument367 pagesGender and Social Policy in A Global Context: Shahra Razavi and Shireen HassimMauro KnovaNo ratings yet
- Gender & GlobalizationDocument25 pagesGender & GlobalizationMaria GordoNo ratings yet
- The Sino-Soviet Relationship Collapsed Due To Ideological Differences. TWEDocument5 pagesThe Sino-Soviet Relationship Collapsed Due To Ideological Differences. TWEMichelle MuirNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide - Cold WarDocument28 pagesRevision Guide - Cold WarMichelle MuirNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide - Cold WarDocument28 pagesRevision Guide - Cold WarMichelle MuirNo ratings yet
- My Christmas Wish - A Personal EssayDocument4 pagesMy Christmas Wish - A Personal EssayMichelle MuirNo ratings yet
- Discussion ClockDocument1 pageDiscussion ClockMichelle MuirNo ratings yet
- The Third Wave of FeminismDocument2 pagesThe Third Wave of FeminismHammad IftikharNo ratings yet
- Tangible and Intangible Cultural HeritageDocument13 pagesTangible and Intangible Cultural HeritageMikko Miks Matining0% (1)
- Feminist Theory in 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesFeminist Theory in 40 CharactersChristian jayr Balcita100% (1)
- Mind Map EDU GenderDocument2 pagesMind Map EDU GenderDevandran DevaNo ratings yet
- Gender Analysis FrameworksDocument26 pagesGender Analysis FrameworksfatimaNo ratings yet
- If You Look at Me Like at A Piece of Meat Then That S A Problem Women in The Center of The Male Gaze Feminist Poststructuralist Discourse Analysis AsDocument18 pagesIf You Look at Me Like at A Piece of Meat Then That S A Problem Women in The Center of The Male Gaze Feminist Poststructuralist Discourse Analysis AsTomaKlusaitėNo ratings yet
- Discipline and Ideas in Social Sciences: PatriarchyDocument3 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in Social Sciences: PatriarchyCin DyNo ratings yet
- Madonna Theory and Capitalist Neosemantic ConstructivismDocument4 pagesMadonna Theory and Capitalist Neosemantic ConstructivismabcarsoNo ratings yet
- Revolutionary Mothers Book Review for HIS 215Document3 pagesRevolutionary Mothers Book Review for HIS 215MonkeyFromMarsNo ratings yet
- The University of Chicago Press Signs: This Content Downloaded From 52.18.63.169 On Mon, 02 Sep 2019 08:10:44 UTCDocument9 pagesThe University of Chicago Press Signs: This Content Downloaded From 52.18.63.169 On Mon, 02 Sep 2019 08:10:44 UTCRodríguez NairdaNo ratings yet
- Jim Crow Laws HomeworkDocument2 pagesJim Crow Laws HomeworkQiying FengNo ratings yet
- Triffles AnalysisDocument4 pagesTriffles AnalysisDurga DeVadassNo ratings yet
- Irigaray V Queer EcofemDocument26 pagesIrigaray V Queer EcofemAnonymous Bh6y0TuVHiNo ratings yet
- Faulkner and Southern SocietyDocument5 pagesFaulkner and Southern Societyapi-279989590No ratings yet
- Final Rhetorical Analysis On Nike AdDocument4 pagesFinal Rhetorical Analysis On Nike Adapi-356962655No ratings yet
- Julia Kristeva S Subversive Semiotic Pol PDFDocument24 pagesJulia Kristeva S Subversive Semiotic Pol PDFSurabHi YadavNo ratings yet
- Works Cited Anthropology Gender FoucaultDocument5 pagesWorks Cited Anthropology Gender FoucaultChristina CharanNo ratings yet
- Waves of Feminism PDFDocument8 pagesWaves of Feminism PDFSajjad Ali AltamashNo ratings yet
- To (O) Queer or Not?: Journal of Lesbian StudiesDocument11 pagesTo (O) Queer or Not?: Journal of Lesbian StudiesMila ApellidoNo ratings yet
- 2018 Entrada InterculturalityDocument20 pages2018 Entrada InterculturalityRosina RosaliNo ratings yet
- Post-Structuralism: Mark Lester B. LamanDocument14 pagesPost-Structuralism: Mark Lester B. LamanMark Lester LamanNo ratings yet
- KKK largely responsible for lack of civil rights progress up to 1941Document2 pagesKKK largely responsible for lack of civil rights progress up to 1941Thomas SeabrookNo ratings yet
- Feminism 130108135914 Phpapp02Document29 pagesFeminism 130108135914 Phpapp02Evita Mae BauNo ratings yet
- Adorno and The Myth of SubjectivityDocument13 pagesAdorno and The Myth of SubjectivityjanpatockaNo ratings yet
- Mercury MagDocument30 pagesMercury MagAnonymous hXQ9MraaBNo ratings yet
- A Streetcar Named DesireDocument147 pagesA Streetcar Named Desirenandini89No ratings yet
- Hegemonic MasculinityDocument12 pagesHegemonic MasculinityIqŕa NooŕNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Summary Mass Communication TheoryDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Summary Mass Communication TheoryAnamta KhanNo ratings yet
- Islam, Sexuality, and The Marginal Positioning of Pengkids and Their Girlfriends in MalaysiaDocument15 pagesIslam, Sexuality, and The Marginal Positioning of Pengkids and Their Girlfriends in MalaysiaBern ChuaNo ratings yet
- Leach CamouflageDocument300 pagesLeach CamouflageStefan KršaninNo ratings yet