Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Manager's Role in Strategic Human Resource Management: Part One - Introduction
Uploaded by
Gangadhar MamadapurOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Manager's Role in Strategic Human Resource Management: Part One - Introduction
Uploaded by
Gangadhar MamadapurCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3
The Manager’s Role
in Strategic Human
Resource Management
Part One | Introduction
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook
publishing as Prentice Hall The University of West Alabama
WHERE WE ARE NOW…
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–2
LEARNING OUTCOMES
1. Explain why strategic planning is important to all
managers.
2. Outline the basic steps in the management planning
process.
3. List the main contents of a typical business plan.
4. Answer the question, “What should a manager do to set
‘smart’ motivational goals?”
5. Explain with examples each of the seven steps in the
strategic planning process.
6. List with examples the main generic types of corporate
strategies and competitive strategies.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–3
LEARNING OUTCOMES (cont’d)
7. Define strategic human resource management and give
an example of strategic human resource management
in practice.
8. Briefly describe three important strategic human
resource management tools.
9. Explain with examples why metrics are essential for
identifying and creating high-performance human
resource policies and practices.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–4
Why Strategic Planning Is Important
To All Managers
• The firm’s strategic plan guides much of what is done by
all to accomplish organizational goals.
• Decisions made by managers depend on the goals set
at each organizational level in support of higher level
goals.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–5
FIGURE 3–1 Sample Hierarchy of Goals Diagram for a Company
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–6
Fundamentals of Management Planning
The Planning Process
1 Set an objective.
2 Make forecasts and check assumptions.
3 Determine/develop alternative courses of action.
4 Evaluate the alternatives.
5 Implement and evaluate your plan.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–7
FIGURE 3–2 Business Plan Table of Contents
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–8
FIGURE 3–3 Acme Consulting Profit and Loss
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–9
How Managers Set Objectives:
SMART Goals
S Specific
M Measureable
A Attainable
R Relevant
T Timely
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–10
How to Set Motivational Goals
Motivational Goal Setting
Assign Assign Assign Encourage
specific measurable challenging but employee
goals goals doable goals participation
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–11
Using Management by Objectives (MBO)
The MBO Process
1 Set overall organizational goals.
2 Set departmental (supporting) goals.
3 Discuss departmental goals with subordinates.
4 Set individual goals and timetables.
5 Give feedback on progress toward goal.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–12
The Strategic Management Process
• Strategy
A course of action the organization intends to pursue to achieve
its strategic aims.
• Strategic Plan
How an organization intends to match its internal strengths and
weaknesses with its external opportunities and threats to
maintain a competitive advantage over the long term.
• Strategic Management
The process of identifying and executing the organization’s
mission by matching its capabilities with the demands of its
environment.
• Leveraging
Capitalizing on a firm’s unique competitive strength while
underplaying its weaknesses.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–13
Business Vision and Mission
• Vision
A general statement of an organization’s intended direction that
evokes emotional feelings in organization members.
• Mission
Spells out who the firm is, what it does, and where it’s headed.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–14
FIGURE 3–4 Management Objectives Grid
Company-Wide or Departmental Objective:
Double sales revenue to $16 million in fiscal year 2011
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–15
FIGURE 3–5 The Strategic Management Process
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–16
FIGURE 3–6 Worksheet for Environmental Scanning
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–17
FIGURE 3–7 SWOT Matrix, with Generic Examples
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–18
FIGURE 3–8 Type of Strategy at Each Company Level
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–19
Types of Corporate Strategies
Corporate Strategy Possibilities
Concentration Diversification Consolidation
Vertical Geographic
integration expansion
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–20
Types of Competitive Strategies
Business-Level
Competitive Strategies
Cost leadership Differentiation Focus/Niche
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–21
Achieving Strategic Fit
• The “Fit” Point of View (Porter)
All of the firm’s activities must be tailored to or fit the chosen
strategy such that the firm’s functional strategies support its
corporate and competitive strategies.
• Leveraging (Hamel and Prahalad)
“Stretch” in leveraging resources—supplementing what you have
and doing more with what you have—can be more important
than just fitting the strategic plan to current resources.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–22
FIGURE 3–9 Southwest Airlines’ Activity System
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–23
Departmental Managers’
Strategic Planning Roles
Department Managers
and Strategy Planning
Formulate
Help devise supporting, Execute
the strategic functional/ the strategic
plan departmental plans
strategies
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–24
Strategic Human Resource Management
• Strategic Human Resource Management
The linking of HRM with strategic goals and objectives in order
to improve business performance and develop organizational
cultures that foster innovation and flexibility.
Involves formulating and executing HR systems—HR policies
and activities—that produce the employee competencies and
behaviors that the company needs to achieve its strategic aims.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–25
FIGURE 3–10 Linking Company-Wide and HR Strategies
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–26
FIGURE 3–11 Basic Model of How to Align HR Strategy
and Actions with Business Strategy
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–27
Strategic HRM Tools
Strategic HRM Tools
Strategy map HR scorecard Digital dashboard
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–28
FIGURE 3–13 Strategy Map for Southwest Airlines
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–29
FIGURE 3–14 The Basic HR Scorecard Relationships
HR activities
Emergent employee
behaviors
Strategically relevant
organizational outcomes
Organizational
performance
Achieve strategic goals
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–30
Creating an HR Scorecard
The 10-Step HR Scorecard Process
Identify required HR policies
1 Define the business strategy 6
and activities
2 Outline value chain activities 7 Create HR Scorecard
Choose HR Scorecard
3 Outline a strategy map 8
measures
Identify strategically required Summarize Scorecard
4 9
outcomes measures on digital dashboard
Identify required workforce 10
5 Monitor, predict, evaluate
competencies and behaviors
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–31
FIGURE 3–15 Three Important Strategic HR Tools
Strategy Map HR Scorecard Digital Dashboard
A graphical tool that A process for managing An information
summarizes the chain of employee performance technology tool that
activities that contribute and for aligning all presents the manager
to a company's success, employees with key with desktop graphs and
and so shows employees objectives, by assigning charts, so he or she gets
the "big picture" of how financial and a picture of where the
their performance nonfinancial goals, company has been and
contributes to achieving monitoring and where it's going, in terms
the company's overall assessing performance, of each activity in the
strategic goals. and quickly taking strategy map.
corrective action.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–32
Building A High-Performance Work System
• High-Performance Work System (HPWS)
A set of human resource management policies and practices
that promote organizational effectiveness.
• High-Performance Human Resource Policies
and Practices
Emphasize the use of relevant HR metrics.
Set out the things that HR systems must do to become an
HPWS.
Foster practices that encourage employee self-management.
Practice benchmarking to set goals and measure the notable
performance differences required of an HPWS.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–33
TABLE 3–1 Comparison of Selected Human Resource Practices in
High-Performance and Low-Performance Companies
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–34
KEY TERMS
business plan offshoring
management by objectives (MBO) strategic human resource
strategic plan management
strategy strategy map
strategic management HR Scorecard
vision statement digital dashboard
mission statement high-performance work system
corporate-level strategy human resource metric
competitive strategy value chain
competitive advantage HR audit
functional strategies
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–35
FIGURE 3–16 Simple Value Chain for “The Hotel Paris”
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–36
FIGURE 3A-1 Simple Value Chain for “The Hotel Paris”
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–37
FIGURE 3A-2 Revenue per FTE (by Industry)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–38
FIGURE 3A-3 2007 Target Bonus Percentage for Executives
(Percent of Total Compensation, by Organizational Size)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–39
FIGURE 3A-4 Sample Metrics from SHRM Measurements Library
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–40
FIGURE 3A-5 Highlights of SHRM® Customized Benchmarking Service
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–41
FIGURE 3A-6 Customized Human Capital Benchmarking Report
for [Your Organization’s Name Here]
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–42
FIGURE 3A-7 Customized Human Capital Benchmarking Report
for [Your Organization’s Name Here]
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–43
TABLE 3–2 Examples of HR System Activities the Hotel Paris Can
Measure as Related to Each Chapter in This Book
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–44
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any
means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Printed in the United States of America.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 3–45
You might also like
- Data AnalysisDocument16 pagesData AnalysisGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- 5092105Document17 pages5092105Gangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Understanding Change: Mba Iv SemDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Change: Mba Iv SemGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic HR Planning & Organizational EffectivenessDocument33 pagesStrategic HR Planning & Organizational EffectivenessGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument20 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Forms of CR and Impact on HRDocument23 pagesForms of CR and Impact on HRGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Dessler Ch1Document45 pagesDessler Ch1Surbhi KumariNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument25 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument17 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Uni T: Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)Document19 pagesUni T: Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)Gangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic HRM FrameworkDocument28 pagesStrategic HRM FrameworkGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument17 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementGangadhar Mamadapur100% (1)
- Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta 2012Document20 pagesFakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta 2012Gangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- 14349954Document14 pages14349954Gangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic HR Vs Traditional HR: Role of HR Is Evolving in Recent YearsDocument18 pagesStrategic HR Vs Traditional HR: Role of HR Is Evolving in Recent YearsGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Learning Management: SystemDocument51 pagesLearning Management: SystemGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic HRM Concepts & InvestmentsDocument13 pagesStrategic HRM Concepts & InvestmentsGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- What Is Strategic HRM?: Has Largely Been Seen As An Administrative Function and As A Cost CenterDocument14 pagesWhat Is Strategic HRM?: Has Largely Been Seen As An Administrative Function and As A Cost CenterGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Concept and Issues: Strategic Human Resources ManagementDocument22 pagesConcept and Issues: Strategic Human Resources ManagementGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Human Resource PlanningDocument51 pagesPresentation On: Human Resource PlanningGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- 9859068Document37 pages9859068Gangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDocument8 pagesStrategic Human Resource ManagementGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Philip Kotler: Distribution Channel-DefinitionDocument64 pagesPhilip Kotler: Distribution Channel-DefinitionGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Learn How LMS Supports Online EducationDocument9 pagesLearn How LMS Supports Online EducationGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Learning Management SystemDocument32 pagesLearning Management SystemFanama Kay100% (3)
- Learning Management: SystemDocument51 pagesLearning Management: SystemGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- 9859068Document37 pages9859068Gangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Human Resource PlanningDocument51 pagesPresentation On: Human Resource PlanningGangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource Management: Chapter No. 8Document31 pagesStrategic Human Resource Management: Chapter No. 8Gangadhar MamadapurNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Manual CleviteDocument180 pagesManual CleviteJacko JaraNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument26 pagesCircuitsDarian ShiNo ratings yet
- Radiscreen-C Coarse Screen BR-ENDocument4 pagesRadiscreen-C Coarse Screen BR-ENmriosqNo ratings yet
- HILTI Direct Fastening Technical Guide - Ed 18Document212 pagesHILTI Direct Fastening Technical Guide - Ed 18rodriguez.gaytanNo ratings yet
- Ekspanzioni VentilDocument6 pagesEkspanzioni VentilNevena AksićNo ratings yet
- CH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsDocument13 pagesCH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsArun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Fall2018Document2 pagesAssignment Fall2018Frans LoekitoNo ratings yet
- LbiDocument13 pagesLbiAac AacNo ratings yet
- D 2320 - 98 R03 RdizmjaDocument3 pagesD 2320 - 98 R03 RdizmjaEliKax!No ratings yet
- R6 Relay ValveDocument2 pagesR6 Relay ValveveereshNo ratings yet
- Contoh Spoof TextDocument7 pagesContoh Spoof TextIndrayaniNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument65 pagesMeasurementChandreshDharDubeyNo ratings yet
- RO-BL-005-Mech-XII-2022 Desmi Pump Hose Radiator Clamp Hose Rubber Gasket Air Filter Dust Strip Curtain Spark LighterDocument2 pagesRO-BL-005-Mech-XII-2022 Desmi Pump Hose Radiator Clamp Hose Rubber Gasket Air Filter Dust Strip Curtain Spark LighterIlyas Rangga RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Section 06 - Hole CleaningDocument81 pagesSection 06 - Hole CleaningRicardo Villar100% (2)
- Airfoil Surface Pressure and Wake Velocity ExperimentDocument24 pagesAirfoil Surface Pressure and Wake Velocity ExperimentAh WenNo ratings yet
- Valvula Relief Pruebas y Ajustes 325blDocument9 pagesValvula Relief Pruebas y Ajustes 325blcristian chuquicondor torresNo ratings yet
- Project Management ProcessDocument23 pagesProject Management ProcessMuhammad Sajid Saeed100% (2)
- Toyota 1ZZ FE 3ZZ FE Engine Repair Manual RM1099E PDFDocument141 pagesToyota 1ZZ FE 3ZZ FE Engine Repair Manual RM1099E PDFJhorwind Requena87% (15)
- Five Nights at Freddy's The Ultimate Guide Five Nights at Freddy's Wiki FandomDocument1 pageFive Nights at Freddy's The Ultimate Guide Five Nights at Freddy's Wiki FandomAmto Hosima0% (1)
- IoT Workshop Tutorial PDFDocument10 pagesIoT Workshop Tutorial PDFSrikanth SriNo ratings yet
- Second Year Hall Ticket DownloadDocument1 pageSecond Year Hall Ticket DownloadpanditphotohouseNo ratings yet
- Amazon Consolidated Interview Experience DocumentDocument4 pagesAmazon Consolidated Interview Experience DocumentNiraj Kumar100% (1)
- CIS ch.5 NotesDocument4 pagesCIS ch.5 NotesClarize R. MabiogNo ratings yet
- IPC-7351A & PCBL Land Pattern Naming ConventionDocument6 pagesIPC-7351A & PCBL Land Pattern Naming ConventionSri ramNo ratings yet
- Airworthiness Directive: Design Approval Holder's Name: Type/Model Designation(s)Document4 pagesAirworthiness Directive: Design Approval Holder's Name: Type/Model Designation(s)Kaung MyatToeNo ratings yet
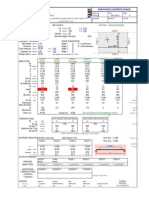
- Raft Slab DesignDocument5 pagesRaft Slab DesignLekins Sefiu Yekini100% (2)
- ASHIDA Product CatalogueDocument4 pagesASHIDA Product Cataloguerahulyadav2121545No ratings yet
- Techrite Siemens Siemens Qra Uv Flame Detection 013060323409Document14 pagesTechrite Siemens Siemens Qra Uv Flame Detection 013060323409Ali Hadi100% (1)
- Data, Information System and Decision MakingDocument24 pagesData, Information System and Decision MakingJanki SwamiNo ratings yet
- RVR & JC College BTech Course Scheme 2012-13Document211 pagesRVR & JC College BTech Course Scheme 2012-13Madhusudhan Rao KNo ratings yet