Professional Documents
Culture Documents
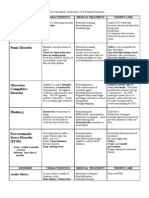
Panic Disorder With Agoraphobia
Uploaded by
VanessaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Panic Disorder With Agoraphobia
Uploaded by
VanessaCopyright:
Available Formats
Panic Disorder with Agoraphobia
a case presentation
vanessa villamia sochat
abnormal psychology
July 11, 2008
Panic Disorder with Agoraphobia An Introduction
Outline
• WHO is our client?
• WHAT are his symptoms and diagnosis?
• WHY did he develop this disorder?
• HOW do we treat it?
Who is our client? John Donahue
DEMOGRAPHICS
CLINICAL HISTORY
• What
Fortyattack
First five
does years
15 years
Johnago ago
think
• Alcoholism
Highofschool principal
his attacks?
• Anxiety
Father ofClinic
three
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
An example of John’s typical panic attack
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
What are his symptoms Diagnosis?
Symptoms of panic attack
Intense apprehension and terror
Impending doom Panic Disorder with
Labored breathing
Heart palpitations Do
Agoraphobia
John’s symptoms fit the
Nausea, chest pain disorder?
Choking and smothering recurrent unexpected
“Anxiety panic attacks
about situations
Dizziness at least 1 of attacks followed by month
Sweating of which would be embarrassing
Trembling or difficult to escape
concern about if panic
having another
Depersonalization attack
symptoms occurred”
Derealization concern about consequences of
Fears of losing control, going crazy
attack
change in behavior because of
attacks
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
What is John’s official DSM-IV-TR diagnosis?
Axis I:
300.21 Panic disorder with agoraphobia
Axis II:
No diagnosis on axis II DMS-IV-TR Diagnosis
Based on:
Axis III: 2)Anxiety about
None situations/events
Axis IV: 3)Avoidance of these
situations/events
Relocation to new state, job change, stressful
work schedule 4)Anxiety not better accounted
for by another disorder!
Axis V:
Global assessment of functioning = 58
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
Why did he develop this disorder?
Integrative Model of Causes and Maintenance of
Panic Disorder
Genetic factors
Social Factors
Etiology of Panic Disorder
Physiological Factors
with Agoraphobia
Cognition (personality)
Life Events “Fear of Fear” Hypothesis
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
Why did he develop this disorder? Genetic factors
Genetic vulnerability to alarm reaction
Psychological problems on mother's side:
* mother alcoholic, panic disorder with agoraphobia
anxious woman constantly concerned with her and her children's
physiological symptoms, worried a lot
* maternal grandfather and two aunts abused alcohol
* maternal grandmother and another aunt - panic disorder
* sister and younger brother, nothing
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
Why did he develop this disorder? social/environment
factors
Stressful environment triggers vulnerability
Physi
Factors
Behavioral Factors
Interoceptive conditioning (learned alarms)
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
Why did he develop this disorder? cognition
Safety behaviors serve to maintain beliefs about the
consequences of panic
Safety behaviors and safety signals
24 access to anti anxiety medication
driving to side of road
holding onto stationary objects
remaining near walls
Lack of control over More attentive to signs
environment of threat
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
Why did he develop this disorder? The big picture
Negative life Psychological
event and biological
vulnerability
Anxiety
Somatic Belief that
symptoms symptoms
dangerous
First panic
GENETIC
attack
SOCIAL/ENVIRONME
Fear symptoms NTAL
BEHAVIORAL
Panic disorder COGNITIVE
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
Why does he still have it?
Summary of maintaining factors panic disorder
panic attack symptoms
agoraphobic situations
cognitions associated with panic attacks
anticipatory anxiety
safety behaviors and signals
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
How do we treat it? In vivo exposure
Exposure treatment
Cognitive behavioral treatment
Panic Control Treatment (PCT)
Situational exposure
(with relaxation technique)
Situational (in vivo) exposure
1) making list of situations that are avoided
2) arranging the list in a hierarchical fashion from least
to most avoided
3) beginning with least difficult situations
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
How do we treat it? Course of treatment
OUTCOME: panic and medication free 6 months after final session
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
Discussion
Why might women outnumber men?
Why do men turn to substance abuse, and women to
avoidance?
How might a psychoanalytical paradigm explain not
perceiving to have a sense of control?
Medication?
Why is remaining in feared situations important for in
vivo exposure?
Public awareness of this disorder?
How would you respond?
Advantages and disadvantages of having spouse/friend?
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
Works Cited
Brown, Timothy. Casebook in abnormal psychology. Thomson
Higher Education, Belmont CA, 2007: 18-35.
Kring, Ann. Abnormal Psychology. John Wiley and Sons,
United States, 20077: 121-155.
Panic Disorder and Agoraphobia.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agoraphobia
WHO WHAT WHY HOW ?
You might also like
- Interviewing The Borderline PatientDocument24 pagesInterviewing The Borderline PatientShona Ray100% (1)
- PsychodynamicsDocument11 pagesPsychodynamicsOrlino PeterNo ratings yet
- Early Identification Psychosis: PrimerDocument16 pagesEarly Identification Psychosis: PrimerGrace LNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Definitions Study GuideDocument2 pagesMental Health Definitions Study GuideTodd ColeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psychopathology PDFDocument5 pagesClinical Psychopathology PDFelvinegunawan50% (2)
- Dimensions of OCD Linked to Intolerance of UncertaintyDocument17 pagesDimensions of OCD Linked to Intolerance of UncertaintySahelNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Psychotic Disorders FinalDocument16 pagesGlossary of Psychotic Disorders FinalYuridiana SánchezNo ratings yet
- Anxiety & Personality DisordersDocument4 pagesAnxiety & Personality Disordersdlneisha61No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Help Is at HandDocument32 pagesSchizophrenia: Help Is at HandAmar DoanxNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument6 pagesAnxiety DisordersSunny Mae100% (1)
- Resilience Framework Adults 2012Document1 pageResilience Framework Adults 2012AMGNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument20 pagesAnxiety DisordersHndrNo ratings yet
- Neuropsych Lec 5 Mental Status ExamDocument2 pagesNeuropsych Lec 5 Mental Status ExamnkivcNo ratings yet
- Goals of the First Therapy SessionDocument8 pagesGoals of the First Therapy Sessionsuhail iqbal sipraNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument25 pagesMental Status ExaminationVishal Makvana AhirNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorder and AddictionDocument31 pagesPersonality Disorder and Addictionraj1090100% (1)
- Apache HelicoptersDocument19 pagesApache HelicoptersSrinidhi Ramachandra AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Risk factors and warning signs of suicide may save livesDocument2 pagesRisk factors and warning signs of suicide may save livesE GNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of SchizophreniaDocument4 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of SchizophreniaNano FelipeNo ratings yet
- GlossaryDocument8 pagesGlossarysnejinka1979No ratings yet
- DementiaDocument21 pagesDementiaYuanita IntanNo ratings yet
- How CBT Effectively Treats DepressionDocument52 pagesHow CBT Effectively Treats DepressionUkhtSameehNo ratings yet
- Psychosis: Ms. Zeina El-Jordi, MSN, RNDocument48 pagesPsychosis: Ms. Zeina El-Jordi, MSN, RNMalak MneimnehNo ratings yet
- Know The Signs PPT 912Document22 pagesKnow The Signs PPT 912John BrooksNo ratings yet
- Coping With Suicidal Thoughts - 2 PDFDocument7 pagesCoping With Suicidal Thoughts - 2 PDFModiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology, Exam I Study CardsDocument12 pagesAbnormal Psychology, Exam I Study CardsVanessa97% (32)
- Play Therapy 1Document1 pagePlay Therapy 1api-496155980No ratings yet
- How to Relax Effectively with CBT SkillsDocument15 pagesHow to Relax Effectively with CBT SkillsDomingo de LeonNo ratings yet
- Handout Chapter15Document3 pagesHandout Chapter15BismahMehdiNo ratings yet
- Rating ScalesDocument4 pagesRating Scalesnkivc100% (3)
- Depression PDFDocument16 pagesDepression PDFMakmur SejatiNo ratings yet
- Models of Abnormality in PsychopathologyDocument18 pagesModels of Abnormality in PsychopathologyGift MwapeNo ratings yet
- Psychology of Thinking Class NotesDocument51 pagesPsychology of Thinking Class NotesVanessa100% (1)
- Hallucinations and Hearing VoicesDocument4 pagesHallucinations and Hearing VoicesCazacu ParascoviaNo ratings yet
- Kübler-Ross stages, alcohol withdrawal signs, lithium monitoringDocument10 pagesKübler-Ross stages, alcohol withdrawal signs, lithium monitoringnicki scheffler100% (2)
- Generalized Anxiety DisorderDocument13 pagesGeneralized Anxiety Disorderapi-3797941100% (1)
- Agoraphobia - Barlow PDFDocument64 pagesAgoraphobia - Barlow PDFRahmat Dedy100% (1)
- Salas vs. CA, 181 SCRA 296, Jan. 22, 1990Document2 pagesSalas vs. CA, 181 SCRA 296, Jan. 22, 1990Jaypoll DiazNo ratings yet
- Psychology 117 Study GuideDocument41 pagesPsychology 117 Study GuideVanessa100% (3)
- Probate of A WillDocument3 pagesProbate of A WillSusanNo ratings yet
- The Bipolar Toolkit by Sarah FreemanDocument25 pagesThe Bipolar Toolkit by Sarah FreemanUsman Aslam ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Depressive DisordersDocument9 pagesDepressive Disorderslengkong100% (1)
- Dreams Are Broken Into Three Parts According To The SunnahDocument19 pagesDreams Are Broken Into Three Parts According To The SunnahpakpidiaNo ratings yet
- Early Onset Psychotic DisordersDocument51 pagesEarly Onset Psychotic Disordersdrkadiyala2100% (1)
- Lopez vs De Los Reyes: House has power to punish for contemptDocument6 pagesLopez vs De Los Reyes: House has power to punish for contemptSofia MoniqueNo ratings yet
- Non-pharmacological Management of Panic Disorder with AgoraphobiaDocument55 pagesNon-pharmacological Management of Panic Disorder with Agoraphobiadrkadiyala2100% (2)
- PSPA3714 Chapter 6 2021Document59 pagesPSPA3714 Chapter 6 2021Kamogelo Makhura100% (1)
- Yolanda Mercado Vs AMA, DigestDocument1 pageYolanda Mercado Vs AMA, DigestAlan Gultia100% (1)
- Neurotransmitter ChartDocument1 pageNeurotransmitter ChartMarieke HagendoornNo ratings yet
- UP Legal Ethics Pre WeekDocument16 pagesUP Legal Ethics Pre WeekWorstWitch TalaNo ratings yet
- PASSFAIL Checklist ComputerDocument2 pagesPASSFAIL Checklist ComputerNiño Bryan AceroNo ratings yet
- Case Vignette Assignment 2Document3 pagesCase Vignette Assignment 2mysteryvan1981No ratings yet
- Pandemic Mental - Learn the Secrets to Stay Positive and Improve your Mental Health During this PandemicFrom EverandPandemic Mental - Learn the Secrets to Stay Positive and Improve your Mental Health During this PandemicNo ratings yet
- Understanding Agoraphobia and its SymptomsTITLEDocument71 pagesUnderstanding Agoraphobia and its SymptomsTITLEEarlyn Joy Sevilla LugoNo ratings yet
- OCPD2Document97 pagesOCPD2regknick100% (1)
- Pharmacotherapy For Generalized Anxiety Disorder in Adults - UpToDate V eDocument14 pagesPharmacotherapy For Generalized Anxiety Disorder in Adults - UpToDate V eMonique GloverNo ratings yet
- EATING DISORDERS: Note Taking OutlineDocument6 pagesEATING DISORDERS: Note Taking OutlinePaula GarciaNo ratings yet
- Outline: PSY 100Y5 Treatment of Disorders Lecture Dr. Kirk R. BlanksteinDocument35 pagesOutline: PSY 100Y5 Treatment of Disorders Lecture Dr. Kirk R. BlanksteinKar GayeeNo ratings yet
- Acute Psychotic DisordersDocument70 pagesAcute Psychotic DisordersDenso Antonius LimNo ratings yet
- Types of AngerDocument14 pagesTypes of AngerMuhammad Amin Amin ButtNo ratings yet
- Define PsychoneuroimmunologyDocument2 pagesDefine PsychoneuroimmunologyYujal Man SinghNo ratings yet
- Anorexia vs Bulimia: Understanding Eating DisordersDocument19 pagesAnorexia vs Bulimia: Understanding Eating DisordersNylia AtibiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia: February 2014Document24 pagesPathophysiology of Schizophrenia: February 2014Tuderici IoanaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersDocument41 pagesSchizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersNoelle Grace Ulep BaromanNo ratings yet
- Why Do Teens Consider Suicide (EAPP)Document5 pagesWhy Do Teens Consider Suicide (EAPP)michaellamigas04No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersDocument49 pagesSchizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersNoelle Grace Ulep BaromanNo ratings yet
- PTSD History and OverviewDocument8 pagesPTSD History and OverviewHellena MaNo ratings yet
- Schizoaffective DisordersDocument12 pagesSchizoaffective DisordersDayle Rj Canson Marquez100% (2)
- Therapeutic Alliance in Schizophrenia The Role of Recovery PDFDocument6 pagesTherapeutic Alliance in Schizophrenia The Role of Recovery PDFAndrei BrookNo ratings yet
- Understanding Anxiety DisordersDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Anxiety DisordersShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- PSYCH101 Lecture 10-11 PsychopathologyDocument80 pagesPSYCH101 Lecture 10-11 PsychopathologyLucy YengNo ratings yet
- MedicareDocument22 pagesMedicareVanessaNo ratings yet
- Narcolepsy As A Disorder of The Hypocretin SystemDocument14 pagesNarcolepsy As A Disorder of The Hypocretin SystemVanessa100% (7)
- A Tale of Two MarketsDocument11 pagesA Tale of Two MarketsVanessa100% (1)
- Depth and Color PerceptionDocument47 pagesDepth and Color PerceptionVanessa100% (6)
- Information Science in Society 100Document13 pagesInformation Science in Society 100Vanessa100% (3)
- The Disparity Between Condom Use and HIV RatesDocument13 pagesThe Disparity Between Condom Use and HIV RatesVanessaNo ratings yet
- Public Policy Midterm I Flash CardsDocument16 pagesPublic Policy Midterm I Flash CardsVanessa100% (1)
- The Element of Trust in Health PolicyDocument10 pagesThe Element of Trust in Health PolicyVanessaNo ratings yet
- Economics 55DDocument6 pagesEconomics 55DVanessa100% (2)
- Public Policy 55D - Final Study GuideDocument18 pagesPublic Policy 55D - Final Study GuideVanessa100% (1)
- Public Policy Midterm II Flash CardsDocument14 pagesPublic Policy Midterm II Flash CardsVanessaNo ratings yet
- Health Policy Class NotesDocument59 pagesHealth Policy Class NotesVanessa100% (3)
- Public Policy 55D Class NotesDocument117 pagesPublic Policy 55D Class NotesVanessa100% (4)
- The Psychology of Thinking Study GuideDocument12 pagesThe Psychology of Thinking Study GuideVanessaNo ratings yet
- Psychology of Thinking Concept ChartDocument5 pagesPsychology of Thinking Concept ChartVanessa100% (2)
- Introduction To Visual CultureDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Visual CultureVanessa100% (2)
- Spouses Ochoa Vs ChinabankDocument4 pagesSpouses Ochoa Vs ChinabankMike E DmNo ratings yet
- Mort Afro Tza TanzaniaDocument2 pagesMort Afro Tza TanzaniaJan TanzaniaNo ratings yet
- People Vs Wong - FulltextDocument2 pagesPeople Vs Wong - Fulltextscartoneros_1No ratings yet
- Approved InstDocument94 pagesApproved Instom vermaNo ratings yet
- Islami Fiqh Masail of The Hairs enDocument23 pagesIslami Fiqh Masail of The Hairs enrubda11No ratings yet
- List Amendments M V Act 23.04.2022Document7 pagesList Amendments M V Act 23.04.2022Diksha MishraNo ratings yet
- When He Texts After Ghosting, Do Not ReplyDocument2 pagesWhen He Texts After Ghosting, Do Not Replymaverick auburnNo ratings yet
- United States v. Neyaunteu Stallings, A.K.A. "Coolio", Milton Lucas, Richard Allen Hepburn, A.K.A. "Al", Walter L. Johnson, A.K.A. "Walt", United States of America v. Eusebio Phelps, A.K.A. "Ebbie", United States of America v. Alex Session, 463 F.3d 1218, 11th Cir. (2006)Document4 pagesUnited States v. Neyaunteu Stallings, A.K.A. "Coolio", Milton Lucas, Richard Allen Hepburn, A.K.A. "Al", Walter L. Johnson, A.K.A. "Walt", United States of America v. Eusebio Phelps, A.K.A. "Ebbie", United States of America v. Alex Session, 463 F.3d 1218, 11th Cir. (2006)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Case BriefDocument11 pagesCase Briefmasroor rehmaniNo ratings yet
- 05&13-Jarantilla v. Jarantilla G.R. No. 154486 December 1, 2010 PDFDocument10 pages05&13-Jarantilla v. Jarantilla G.R. No. 154486 December 1, 2010 PDFJopan SJNo ratings yet
- Spec Pro Cases - Batch 3Document275 pagesSpec Pro Cases - Batch 3Azrael CassielNo ratings yet
- Quick Point-By-Point Summary of Duterte's SONA 2019: High Approval RatingsDocument4 pagesQuick Point-By-Point Summary of Duterte's SONA 2019: High Approval RatingsRhodaNo ratings yet
- BodoDocument10 pagesBodoTanmoi BaishyaNo ratings yet
- Silence The Court Is in Session by Vijay Tendulkar 39Document14 pagesSilence The Court Is in Session by Vijay Tendulkar 39Chaitanya Shekhar 7110% (1)
- What Are The Key Features of The US Political System?Document11 pagesWhat Are The Key Features of The US Political System?Yuvraj SainiNo ratings yet
- COA authority to recommend filing of casesDocument2 pagesCOA authority to recommend filing of casesasg_jingNo ratings yet
- Carter TimelineDocument1 pageCarter Timelinehoneyl5395No ratings yet
- MIRANDA v. ERNESTODocument2 pagesMIRANDA v. ERNESTOEmmanuel Princess Zia SalomonNo ratings yet
- Python Pour Hackers - BootcampDocument46 pagesPython Pour Hackers - BootcampLorem IpsumNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense GuideDocument9 pagesPresent Simple Tense GuideGustavo PacompiaNo ratings yet
- Science and Faith at LourdesDocument8 pagesScience and Faith at LourdesBr. Paul Nguyen, OMVNo ratings yet
- Civil Code on Common CarriersDocument5 pagesCivil Code on Common CarriersDey DiazNo ratings yet