Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2010 Macro FRQ
Uploaded by
Kripansh GroverOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2010 Macro FRQ
Uploaded by
Kripansh GroverCopyright:
Available Formats
Norman
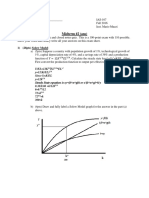
1.[10 total points] AssumethattheU.S.economyiscurrentlyinlong-runequilibrium. (a)[2pts]Drawacorrectlylabeledgraphofaggregatedemandandaggregatesupply andshoweachofthefollowing. (i)Thelong-runaggregatesupplycurve (ii)Thecurrentequilibriumoutput&PL,labeledasYEandPLE,respectively.
PL
PL2 PLE
AD1
LRAS SRAS
E2 E1
AD2
Answer 1(a)(i): 1 pt for correctly labeled graph with downward-sloping AD, upward-sloping SRAS, PLE and YE. (ii) 1 pt for showing a vertical LRAS at YE.
YE YI Real GDP
(b)[2pts]Assumethatthegovernmentincreasesspendingonnationaldefensewithout raisingtaxes. (i)Onyourgraphinpart(a),showhowthegovernmentactionaffectsAD. (ii)Howwillthisgovernmentactionaffecttheunemploymentrateintheshortrun? Explain. Answer: 1. (b) (i) As can be seen on the graph, the increase in G would increase AD to AD2, increasing PL and Y. 1. (b) (II) The increase in AD to AD2 would decrease unemployment in the short run, as the increase in AD would lead to an increase in output & profits, resulting in more workers being hired and therefore the decrease in unemployment.
1.(c)[2pts]Assumethattheeconomyadjuststoanewlong-runequilibriumafterthe increaseingovernmentspending. (i)Howwilltheshort-runaggregatesupplycurveinthenewlong-runequilibrium comparewiththatintheinitiallong-runequilibriuminpart(a)?Explain. (ii)Onyourgraphinpart(a),labelthenewlong-runequilibriumpricelevelasPL2. LRAS
PL
PL2 PLE
SRAS2 SRAS1
E2 E1
AD
YE YI Real GDP
Answer 1.(c)(i): 1 pt for stating that the SRAS will shift to the left because the Increase in AD would result in more inflation so workers will demand higher wages AND showing PL2 correctly in part (a)s graph. 1.(c)(ii) 1 pt for explaining that the actual PL is higher than the expected PL, or wages and commodity prices adjust to higher PL[flexible wages], causing the SRAS curve to shift to the left.
1.(d)[2pts]Inordertofinancetheincreaseingovernmentspendingonnationaldefense frompart(b),thegovernmentborrowsfundsfromthepublic.Usingacorrectly labeledgraphoftheloanablefundsmarket,showtheeffectofthegovernments borrowingontherealinterestrate. (e)[2pts]Giventhechangeintherealinterestrateinpart(d),whatistheimpact oneachofthefollowing? Answer to 1. (d) 1 pt for correctly labeled graph (i)Investment of the LFM. (ii)Economicgrowthrate.Explain. 1 pt for showing a rightward shift of the demand
Real Interest Rate, (%)
D2 LFM D1 S
E2 E1
1 pt for showing a rightward shift of the demand curve resulting in a higher interest rate OR a leftward shift of the supply curve resulting in a higher RIR.
r2 r1
Quantity of Loanable Funds F1 F2 Answer to 1. (e) (i) [1 pt] The higher RIR will result in less investment in tools and machinery. 1. (e) (ii) [1 pt] The decrease in tools and machinery will decrease overall productivity and economic growth [capital stock].
2.[6 total points] Adropincreditcardfeescausespeopletouse creditcardsmoreoftenfortransactionsanddemandlessmoney. (a)[2pts]Usingacorrectlylabeledgraphofthemoneymarket,showhowthenominal interestratewillbeaffected. (b)[1pt]Giventheinterestratechangeinpart(a),whatwillhappentobondpricesin theshortrun?
Nominal Interest Rate
Dm
n1
MS
Answer to 2. (a) The decrease in Dt for money would decrease the Dm curve resulting in a lower NIR and RIR. 2. (b) Bond prices are inverse to the interest rate so bond prices would increase
Answer to 2. (c) The lower IR will increase AD due to more investment and interest n2 sensitive consumption [the lower IR would Dm2 also depreciate the dollar and increase Xn]. All 3 cause an increase in AD & PL in the SR. Quantity of Money 2. (d) Selling bonds would be the OMO as [Money Market] it would decr MS, incr NIR and decr AD & PL.
(c)[2pt]Giventheinterestratechangeinpart(a),whatwillhappentothepricelevel intheshortrun?Explain. (d)[1pt]Identifyanopen-marketoperationtheFedcouldusetokeepthenominalinterest rateconstantatthelevelthatexistedbeforethedropincreditcardfees.Explain.
3.[6 total points] AU.S.firmsells$10millionworthofgoodstoafirmin Argentina,wherethecurrencyisthepeso. (a)[1pt]HowwillthetransactionaboveaffectArgentinasaggregate demand?Explain. (b)[1pt]AssumethattheU.S.currentaccountbalancewithArgentinais initiallyzero.HowwillthetransactionaboveaffecttheUnitedStates current accountbalance?Explain. Answer to 3. (a) The selling of $10 M of U.S. goods to Argentina would decrease Argentinas net exports which would decrease their AD. AD = C+I+G+X-M, when M gets larger, GDP gets smaller. 3. (b) The $10 million increase in net exports would cause a flow of $10 million worth of pesos into the U.S. [recorded as a +$10 million] and would cause a current account balance of ZERO to become a +$10 million surplus account balance.
Price
Peso Price of Dollar
Plookingfor$s $slookingforP E2 P100
P50
D1$
S2$
S1$
Answer to 3. (c) (i): If the U.S. decrease financial investment
in Argentina, the U.S. would decrease their supply of
dollars to Argentina, resulting
Peso
depreciates
E1
in a decrease in demand for the peso. (c) (ii) As shown on the graph,
the dollar would appreciate.
Quantity of Dollars
(d) The cheaper prices in the U.S. will result in more demand for U.S. goods and therefore the dollar, appreciating the dollar and depreciating the peso.
3.(c)[2pt]UsingacorrectlylabeledgraphoftheforeignexchangemarketfortheU.S. dollar,showhowadecreaseintheU.S.financialinvestmentinArgentinaaffectseach. (i)ThesupplyofUnitedStatesdollars (ii)ThevalueoftheUnitedStatesdollarrelativetothepeso (d)[2pt]Supposethattheinflationrateis3%intheU.S.and5%inArgentina. WhatwillhappentothevalueofthepesorelativetotheUnitedStatesdollaras aresultofthedifferenceininflationrates? Explain.
Econ
2010 FRQ
How To S core Well On F RQs FRQs for Dummies
FRQs
Animationeconomics.com
You might also like
- Targeted Inflation Rate, NIR, RIRDocument8 pagesTargeted Inflation Rate, NIR, RIRwakemeup143No ratings yet
- PAPER 2 PRACTICE 1 - Macroeconomics - With MarkschemeDocument12 pagesPAPER 2 PRACTICE 1 - Macroeconomics - With MarkschemeKayleen PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Efficiency, Equity and The Role of GovernmentDocument7 pagesTopic 5 Efficiency, Equity and The Role of GovernmenttristachanNo ratings yet
- Use The Table Below To Answer The Following QuestionDocument9 pagesUse The Table Below To Answer The Following QuestionexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Pre AP Economics - FinalDocument6 pagesPre AP Economics - FinalRebecca NiezenNo ratings yet
- Fei2123PS2 PDFDocument4 pagesFei2123PS2 PDFMarco ChanNo ratings yet
- Macro Term Test 1415 Oct (Final)Document7 pagesMacro Term Test 1415 Oct (Final)Nicholas Giovanna ChongNo ratings yet
- U6018+Practice+Midterm+Exam Spring+2022 SolsDocument6 pagesU6018+Practice+Midterm+Exam Spring+2022 SolsKaren QNo ratings yet
- Macro Modified FRQs For 2020 Exam No GraphsDocument17 pagesMacro Modified FRQs For 2020 Exam No GraphsShirin JNo ratings yet
- Phillips Curve FRQs AnswersDocument6 pagesPhillips Curve FRQs AnswersDuck520100% (1)
- Macroeconomics Midterm Exam KeyDocument8 pagesMacroeconomics Midterm Exam Keyshush10No ratings yet
- IAS 107 Midterm #2 Answers 2016Document11 pagesIAS 107 Midterm #2 Answers 2016Carol YaoNo ratings yet
- Ec 392 PS 2Document1 pageEc 392 PS 2Pablo MercadoNo ratings yet
- E - Portfolio Assignment-1Document7 pagesE - Portfolio Assignment-1api-280064053No ratings yet
- Macro90: N Employed Labour ForceDocument10 pagesMacro90: N Employed Labour ForceGary LamNo ratings yet
- Fei 2123 PS3Document4 pagesFei 2123 PS3MarcoNo ratings yet
- Answer ALL The Questions in Section A and TWO Questions From Section BDocument6 pagesAnswer ALL The Questions in Section A and TWO Questions From Section BTom WongNo ratings yet
- Exam 2014 With Memo PDFDocument46 pagesExam 2014 With Memo PDFTumi Mothusi100% (1)
- 2008 Macro FRQDocument8 pages2008 Macro FRQsachinneha143No ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument4 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionTrúc LinhNo ratings yet
- University of Melbourne Economics Exam ReviewDocument10 pagesUniversity of Melbourne Economics Exam ReviewA SunNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Test Question PoolDocument6 pagesTutorial Test Question PoolAAA820No ratings yet
- 8.0money Demand & Money MKT EquilibriumDocument16 pages8.0money Demand & Money MKT EquilibriumJacquelyn ChungNo ratings yet
- Fei2123PS4 PDFDocument4 pagesFei2123PS4 PDFMarco ChanNo ratings yet
- ECO3002 AssignmentsDocument6 pagesECO3002 AssignmentsanthsamNo ratings yet
- Problem Set #4 Macroeconomics Solutions Due December 6thDocument7 pagesProblem Set #4 Macroeconomics Solutions Due December 6thSteven Hyosup KimNo ratings yet
- FM423 Practice Exam IIIDocument7 pagesFM423 Practice Exam IIIruonanNo ratings yet
- Eco102-1 Final-Sp21Document2 pagesEco102-1 Final-Sp21Pranta RoyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 EECF1624 2022 MemoDocument10 pagesTutorial 2 EECF1624 2022 MemoTshegofatso MatlalaNo ratings yet
- March Macro Econ Exam 1022Document19 pagesMarch Macro Econ Exam 1022Kevin KobayashiNo ratings yet
- Final Exam MACRO Jan 21 2019Document4 pagesFinal Exam MACRO Jan 21 2019benrjebfatma18No ratings yet
- Eco104 Mid-TermDocument3 pagesEco104 Mid-TermNaeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics policies and choicesDocument3 pagesMacroeconomics policies and choicesmary aligmayoNo ratings yet
- EC3102 Macroeconomic Analysis II Questions and Answers Prepared by Ho Kong Weng Tutorial 10Document5 pagesEC3102 Macroeconomic Analysis II Questions and Answers Prepared by Ho Kong Weng Tutorial 10Chiew Jun Siew0% (1)
- FPDocument13 pagesFPKenny KwokNo ratings yet
- Exam1 Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesExam1 Review QuestionsOpen ThedorNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Assignment 2Document4 pagesMacroeconomics Assignment 2reddygaru1No ratings yet
- Ema3572 2015 11 NorDocument6 pagesEma3572 2015 11 NorNambahu PinehasNo ratings yet
- Sample Economics Question PaperDocument17 pagesSample Economics Question PaperRavikumar BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- AP Macro Problem Set 3 StudentDocument2 pagesAP Macro Problem Set 3 Studentspfitz11No ratings yet
- Fei2123PS2 Soln PDFDocument9 pagesFei2123PS2 Soln PDFMarco ChanNo ratings yet
- LV 2 Economics 2023 91224 Analyse Economic Growth Using Economic Concepts and Models 0140129063 - Vadim FongDocument2 pagesLV 2 Economics 2023 91224 Analyse Economic Growth Using Economic Concepts and Models 0140129063 - Vadim FongVadim FongNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions FinalDocument3 pagesPractice Questions FinalAman SinghNo ratings yet
- ECON 203 Midterm 2013W FaisalRabbyDocument7 pagesECON 203 Midterm 2013W FaisalRabbyexamkillerNo ratings yet
- 201 - Winter08 - Final Solutions PDFDocument13 pages201 - Winter08 - Final Solutions PDFpenusilaNo ratings yet
- Chapters 8,11 & 12Document9 pagesChapters 8,11 & 12gg ggNo ratings yet
- ECO 441 Homework #1: IS-MP, Mundell-Fleming, Cobb-DouglasDocument1 pageECO 441 Homework #1: IS-MP, Mundell-Fleming, Cobb-DouglasthitNo ratings yet
- PS1 Answers Macroeconomic TheoryDocument2 pagesPS1 Answers Macroeconomic TheorymiguealsilvaruizNo ratings yet
- Quiz EconomicsDocument4 pagesQuiz EconomicsSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Exam #3Document9 pagesECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Exam #3sianhbgNo ratings yet
- Tutorial5 RE1704 AY22 23Document37 pagesTutorial5 RE1704 AY22 23Lim JonathanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Economics Sample Paper-07Document7 pagesCBSE Class 11 Economics Sample Paper-07cbsestudymaterialsNo ratings yet
- Model Examination 2010-2011 EconomicsDocument2 pagesModel Examination 2010-2011 Economicssharathk916No ratings yet
- ECON 202 - Assignment 3-Section III-No Answer KeyDocument4 pagesECON 202 - Assignment 3-Section III-No Answer KeyArodwenNo ratings yet
- Int Macro 2020 Exam 1 CorrDocument3 pagesInt Macro 2020 Exam 1 CorrLiu Huanyue EricNo ratings yet
- E - Portfolio AssignmentDocument3 pagesE - Portfolio Assignmentapi-252922808No ratings yet
- Money and Monetary PolicyDocument3 pagesMoney and Monetary PolicyTom Schenk Jr.No ratings yet
- China's Trump Card: Cryptocurrency and its Game-Changing Role in Sino-US TradeFrom EverandChina's Trump Card: Cryptocurrency and its Game-Changing Role in Sino-US TradeNo ratings yet
- Asset Rotation: The Demise of Modern Portfolio Theory and the Birth of an Investment RenaissanceFrom EverandAsset Rotation: The Demise of Modern Portfolio Theory and the Birth of an Investment RenaissanceNo ratings yet
- FAke Note Detection SchemeDocument1 pageFAke Note Detection SchemeKripansh GroverNo ratings yet
- As-11-Accounting For The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange RatesDocument24 pagesAs-11-Accounting For The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange RatesKripansh GroverNo ratings yet
- Mix PlanningDocument11 pagesMix PlanningKripansh GroverNo ratings yet
- Commodity BreakDocument3 pagesCommodity BreakKripansh GroverNo ratings yet
- Referencegroupsandfamilyinfluences 110223194656 Phpapp02Document23 pagesReferencegroupsandfamilyinfluences 110223194656 Phpapp02Deve CroosNo ratings yet
- Coca ColaDocument36 pagesCoca ColaKripansh Grover0% (2)
- Report ComDocument3 pagesReport ComKripansh GroverNo ratings yet
- 21 Culture & Sub CultureDocument18 pages21 Culture & Sub Culturevibinas23No ratings yet
- Sharekhan top picks outperform in FY2010Document6 pagesSharekhan top picks outperform in FY2010Kripansh GroverNo ratings yet
- Euro Euro: System SystemDocument57 pagesEuro Euro: System SystemKripansh GroverNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Development Centre Studies: The Rise of China and India: What's in It For Africa?Document5 pagesDevelopment Centre Studies: The Rise of China and India: What's in It For Africa?Kripansh GroverNo ratings yet
- Basic Macroeconomic ConceptsDocument3 pagesBasic Macroeconomic ConceptsAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Start-Up Business Plan for Agricultural Export CooperativeDocument34 pagesStart-Up Business Plan for Agricultural Export CooperativeAbenet100% (2)
- 10 Principle of EconomicsDocument4 pages10 Principle of EconomicsAli RAZANo ratings yet
- A Case of Bad Good News (A - Newsweek) 1983 09 26Document2 pagesA Case of Bad Good News (A - Newsweek) 1983 09 26pedronuno20No ratings yet
- DoccDocument25 pagesDoccSagarNo ratings yet
- Wallstreetjournal 20190730 TheWallStreetJournalDocument32 pagesWallstreetjournal 20190730 TheWallStreetJournalbadugaNo ratings yet
- Remittance and Its Economic Impacts On BangladeshDocument16 pagesRemittance and Its Economic Impacts On BangladeshM A Akad MasudNo ratings yet
- Scert: 12 Economy Chapter-5Document23 pagesScert: 12 Economy Chapter-5tamilrockers downloadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document43 pagesLecture 10Robert M. MitchellNo ratings yet
- Daniel L Landau 1985Document20 pagesDaniel L Landau 1985Americo Sanchez Cerro MedinaNo ratings yet
- ECO415 Tutorial Questions on Macroeconomics Chapters 7 and 8Document3 pagesECO415 Tutorial Questions on Macroeconomics Chapters 7 and 8anis izzatiNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF RISKS EXPLAINEDDocument7 pagesTYPES OF RISKS EXPLAINEDsanu gawaliNo ratings yet
- The Case For Investing in South AfricaDocument120 pagesThe Case For Investing in South AfricaBusinessTech100% (7)
- 3.2.2 Answer Key To Data Response Questions On Exchange RatesDocument5 pages3.2.2 Answer Key To Data Response Questions On Exchange RatesI-Zac LeeNo ratings yet
- Intro To Christian Economics PDFDocument425 pagesIntro To Christian Economics PDFJanderson BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Political Economy Annotated BibliographyDocument3 pagesPolitical Economy Annotated BibliographyAndrew S. Terrell100% (1)
- Share & Business Valuation Case Study Question and SolutionDocument6 pagesShare & Business Valuation Case Study Question and SolutionSarannyaRajendraNo ratings yet
- Economics Concepts and PrinciplesDocument19 pagesEconomics Concepts and Principleswenatchee25No ratings yet
- Financial Analysis: Learning ObjectivesDocument39 pagesFinancial Analysis: Learning ObjectivesKeith ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Money Credit and Banking PDFDocument40 pagesMoney Credit and Banking PDFmark joseph mayorNo ratings yet
- FIN444 Part2 (Final)Document22 pagesFIN444 Part2 (Final)A ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Keynes and the Failure of Self-Correction in the Classical ViewDocument29 pagesKeynes and the Failure of Self-Correction in the Classical ViewCatarina DuarteNo ratings yet
- Market Wrap PUBLIC BANKDocument4 pagesMarket Wrap PUBLIC BANKzarifmasriNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 1 Economics - Our Cheat Sheet - 300hoursDocument22 pagesCFA Level 1 Economics - Our Cheat Sheet - 300hoursMichNo ratings yet
- Syllabus AD312 - Spring23Document3 pagesSyllabus AD312 - Spring23Ekin MadenNo ratings yet
- Zangi TestDocument20 pagesZangi TestEng Hinji RudgeNo ratings yet
- TaxDocument43 pagesTaxVNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics Chapter 30 Key Concept - Macroeconomic ObjectivesDocument2 pagesIGCSE Economics Chapter 30 Key Concept - Macroeconomic ObjectivesemilyNo ratings yet
- AP 宏观经济学 2019Document47 pagesAP 宏观经济学 2019Jacob Xiao100% (1)
- 2016 Economics H2 JC2 Pioneer Junior CollegeDocument14 pages2016 Economics H2 JC2 Pioneer Junior CollegeSebastian ZhangNo ratings yet