Professional Documents
Culture Documents
By Dinesh Sundaram Keerthi Sagar Prabhu Prithviraj Sindhu V.Vaikunth
Uploaded by
Sindhu ViswanathanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
By Dinesh Sundaram Keerthi Sagar Prabhu Prithviraj Sindhu V.Vaikunth
Uploaded by
Sindhu ViswanathanCopyright:
Available Formats
By Dinesh Sundaram Keerthi Sagar Prabhu Prithviraj Sindhu V.
Vaikunth
Team 10
2/14/2011
Topic Recession Introduction GDP Growth Elements of concern Growth rate in 2010 Govt.s debt burden Three speeds
Slide no. 3 5 7 10 12 13 19
Dark clouds
Twin dangers
21
23
Team 10
2/14/2011
A Recession is a contraction phase of the business cycle. National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) is the official agency in charge of declaring that the economy is in a state of recession. An economy typically expands for 6-10 years and tends to go into a recession for about 6 months to 2 years
Team 10
2/14/2011
Team 10
2/14/2011
The Business Cycle Dating Committee of The National Bureau of Economic Research in U.S. had dated the recession induced by financial crisis to December 2007. The recession, estimated to have lasted 18 months without signs of robust recovery.
Team 10
2/14/2011
To overcome recession: Governments expanded expenditures.
Central banks pumped in liquidity to save the financial system and restore demand.
Team 10
2/14/2011
Taking the world as a whole: 2006 -> More than 5% 2007 -> Dipped to 2.8% 2008 & 2009 -> -0.6% 2010 -> Recovered to 4.8%.
Team 10
2/14/2011
14
12
10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 -4 -6 2006
2007
2008 2009 2010
Team 10
2/14/2011
Speed and nature of recovery. In spite of positive growth, job losses were not being fully recovered and the unemployment rate remained high. In 2010, the unemployment rate touched 10% in U.S. and France.
Team 10
2/14/2011
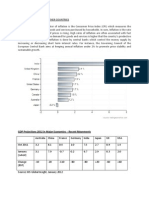
Growth was extremely unevenly distributed across regions and nations.
Recovery appear to be largely restricted to a few emerging market countries. Inflation is high in countries where the growth rate is higher when compared to other countries.
Team 10
2/14/2011
10
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Newly industrialized Asian economies Excluding G7 and 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 Euro union G7 World
Team 10
2/14/2011
11
Developing countries -> 7.1% G7 countries -> 2.5%
European union -> 1.7%
Team 10
2/14/2011
12
Subprime mortgage crisis (home loan defaults). Increased debt on the balance sheets of the government in the developed countries like U.S.
Team 10
2/14/2011
13
Increase the reticence of govt. to substitute public for private expenditure as the stimulus to growth.
Unevenness in growth which was earlier seen as a sign of global imbalance, is now being celebrated as a cause for optimism.
Team 10
2/14/2011
14
Team 10
2/14/2011
15
Team 10
2/14/2011
16
Team 10
2/14/2011
17
Team 10
2/14/2011
18
Three speeds at which the recovery is expected to proceed during 2011:
6% or more in the emerging economies led by China and India. 3% growth in U.S. Less than 2% growth in European union.
Team 10
2/14/2011
19
Factors affecting balanced recovery are:
When growth is there, unemployment should also get reduced.
Lack of confidence due to cheap liquidity into the system. Recovery generated by developments such as the sovereign debt problems in Europe is partly responsible.
Team 10
2/14/2011
20
Those emerging markets recording the highest rates of growth are experiencing symptoms of overheating in the form of inflation in goods and/or asset prices In China, inflation stood at 5.1% in 2010 when the growth rate crossed 10%.
Team 10
2/14/2011
21
Housing prices also rose to 7.8%.
In India the growth has been accompanied with inflation. In addition, across emerging markets, the inflow of foreign capital fuelled by the availability of cheap credit in the developed countries is resulting in currency appreciation that undermines export competitiveness and hurts growth.
Team 10
2/14/2011
22
Recovery to be financed with debt that makes it vulnerable. The growth in U.S. consumer spending might encourage emerging markets to return to relying on export led growth.
Team 10
2/14/2011
23
www.wikipedia.com www.tradingeconomics.com
Team 10
2/14/2011
24
Team 10
2/14/2011
25
You might also like
- EcR - 1 Leading and Lagging IndicatorsDocument10 pagesEcR - 1 Leading and Lagging IndicatorsMiloš ĐukićNo ratings yet
- Journalize The Following Transactions in The Journal Page Below. Add Explanations For The Transactions and Leave A Space Between EachDocument3 pagesJournalize The Following Transactions in The Journal Page Below. Add Explanations For The Transactions and Leave A Space Between EachTurkan Amirova100% (1)
- Executive Summary: The Global OutlookDocument34 pagesExecutive Summary: The Global OutlookmarrykhiNo ratings yet
- Mufon Ufo JournalDocument21 pagesMufon Ufo JournalSAB78No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fast SwimmingDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Fast SwimmingTorcay Ulucay100% (1)
- of Types of Nuclear ReactorDocument33 pagesof Types of Nuclear Reactormandhir67% (3)
- Siemens MV Gas Insulated Switch GearDocument14 pagesSiemens MV Gas Insulated Switch GearSajesh Thykoodan T VNo ratings yet
- Space Analysis in Orthodontic: University of GlasgowDocument16 pagesSpace Analysis in Orthodontic: University of GlasgowNizam Muhamad100% (1)
- UMR Introduction 2023Document110 pagesUMR Introduction 2023tu reves mon filsNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDocument59 pagesPlacenta Previa Case StudySiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- 1 Colmac DX Ammonia Piping Handbook 4th EdDocument64 pages1 Colmac DX Ammonia Piping Handbook 4th EdAlbertoNo ratings yet
- RTG E-One - Manual de Manutenção 41300-41303 (EN)Document328 pagesRTG E-One - Manual de Manutenção 41300-41303 (EN)Conrado Soares100% (1)
- Euro Crisis Impact on IndiaDocument18 pagesEuro Crisis Impact on Indiaडॉ. शुभेंदु शेखर शुक्लाNo ratings yet
- Securities Market in India: An OverviewDocument15 pagesSecurities Market in India: An OverviewShailender KumarNo ratings yet
- World Economy 2011Document48 pagesWorld Economy 2011Arnold StalonNo ratings yet
- World Economic Situation and Prospects 2011Document48 pagesWorld Economic Situation and Prospects 2011Iris De La CalzadaNo ratings yet
- The Forces Shaping The Economy Over 2012Document10 pagesThe Forces Shaping The Economy Over 2012economicdelusionNo ratings yet
- World Economy in 2010 Yearly ReviewDocument5 pagesWorld Economy in 2010 Yearly ReviewJohn Raymond Salamat PerezNo ratings yet
- 4feb11 Retrospectiva2010 Scenarii2011 PDFDocument16 pages4feb11 Retrospectiva2010 Scenarii2011 PDFCalin PerpeleaNo ratings yet
- International Monetary Fund: Hina Conomic UtlookDocument10 pagesInternational Monetary Fund: Hina Conomic UtlooktoobaziNo ratings yet
- 18 Econsouth Fourth Quarter 2012Document6 pages18 Econsouth Fourth Quarter 2012caitlynharveyNo ratings yet
- Vietnam's Key Economic Indicators and Stabilization MeasuresDocument4 pagesVietnam's Key Economic Indicators and Stabilization MeasuresMc ElNo ratings yet
- APEC Economic Trends Analysis: APEC Policy Support UnitDocument18 pagesAPEC Economic Trends Analysis: APEC Policy Support UnitManu NuñezNo ratings yet
- Ciptadana Outlook 2012Document44 pagesCiptadana Outlook 2012adisthya_rNo ratings yet
- Massive Global Stimulus Needed to Counter DownturnDocument4 pagesMassive Global Stimulus Needed to Counter DownturnRahul YenNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Developments and Securities MarketsDocument16 pagesMacroeconomic Developments and Securities MarketsJugal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis: Is The Recovery Sustainable?Document16 pagesStrategic Analysis: Is The Recovery Sustainable?varj_feNo ratings yet
- Monthly: La Reforma Del Sector Servicios OUTLOOK 2012Document76 pagesMonthly: La Reforma Del Sector Servicios OUTLOOK 2012Anonymous OY8hR2NNo ratings yet
- 2011 Sovereign Credit Risk Outlook: Dagong Global Credit Rating Co., LTDDocument18 pages2011 Sovereign Credit Risk Outlook: Dagong Global Credit Rating Co., LTDrichardck61No ratings yet
- Global PerpectiveDocument3 pagesGlobal Perpectivessharma_895257No ratings yet
- Country Intelligence: Report: TaiwanDocument22 pagesCountry Intelligence: Report: TaiwanSumanthKambhammettuNo ratings yet
- Bahrain Economy 2012Document54 pagesBahrain Economy 2012Usman MoonNo ratings yet
- Brazil Russia India China South AfricaDocument3 pagesBrazil Russia India China South AfricaRAHULSHARMA1985999No ratings yet
- Macro Economic and Monetary Developments First Quarter Review 2011-12Document62 pagesMacro Economic and Monetary Developments First Quarter Review 2011-12abinash229138No ratings yet
- Pakistan Economic Survey 2010 2011Document272 pagesPakistan Economic Survey 2010 2011talhaqm123No ratings yet
- Chap1 OverviewDocument20 pagesChap1 Overviewamolsam1No ratings yet
- Bahrain Economic Quarterly: Second Quarter 2012Document54 pagesBahrain Economic Quarterly: Second Quarter 2012GeorgeNo ratings yet
- c1 PDFDocument11 pagesc1 PDFDanish CooperNo ratings yet
- Economic Outlook Q2 2011Document5 pagesEconomic Outlook Q2 2011Mark PaineNo ratings yet
- G R o U P o F T W e N T Y: M G - 2 0 D J 1 9 - 2 0, 2 0 1 2 M CDocument20 pagesG R o U P o F T W e N T Y: M G - 2 0 D J 1 9 - 2 0, 2 0 1 2 M CLuke Campbell-SmithNo ratings yet
- Jonathan S 2012 Budget Speech Before The National AssemblyDocument27 pagesJonathan S 2012 Budget Speech Before The National Assembly25121962No ratings yet
- Euro Crisis - Eco (Compiled and Formatted)Document16 pagesEuro Crisis - Eco (Compiled and Formatted)Rahul GoyalNo ratings yet
- November 2011 - Volume 16 - No. 8: Confederation of Indian IndustryDocument32 pagesNovember 2011 - Volume 16 - No. 8: Confederation of Indian IndustryteslaaaNo ratings yet
- Interim Economic Outlook: Puzzles and UncertaintiesDocument8 pagesInterim Economic Outlook: Puzzles and Uncertaintiesapi-296228558No ratings yet
- SEB Asia Corporate Bulletin: MayDocument7 pagesSEB Asia Corporate Bulletin: MaySEB GroupNo ratings yet
- Add From The First Half of The Print OutsDocument4 pagesAdd From The First Half of The Print OutsAteev SinghalNo ratings yet
- Key Issues in The Global Economy 2011: Lecture Two AUGUST 2011Document109 pagesKey Issues in The Global Economy 2011: Lecture Two AUGUST 2011MiltonThitswaloNo ratings yet
- 2011-12 Monetary PolicyDocument21 pages2011-12 Monetary PolicyNitinAggarwalNo ratings yet
- Bos Canada White Paper Final SHRTPPDocument36 pagesBos Canada White Paper Final SHRTPPEsiKamranNo ratings yet
- IMF World Economic and Financial Surveys Consolidated Multilateral Surveillance Report Sept 2011Document12 pagesIMF World Economic and Financial Surveys Consolidated Multilateral Surveillance Report Sept 2011babstar999No ratings yet
- First Quarter Review of Monetary Policy 2012-13: Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument18 pagesFirst Quarter Review of Monetary Policy 2012-13: Reserve Bank of IndiaProfessor Sameer KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 2012 Budget PublicationDocument71 pages2012 Budget PublicationPushpa PatilNo ratings yet
- CHAP 1 IntroductionDocument5 pagesCHAP 1 IntroductionyaswayanadNo ratings yet
- October 2012 Volume XII Number 2Document116 pagesOctober 2012 Volume XII Number 2Kyren GreiggNo ratings yet
- Euro Crisis's Impact On IndiaDocument49 pagesEuro Crisis's Impact On IndiaAncy ShajahanNo ratings yet
- Rollback of StimulusDocument7 pagesRollback of Stimulusamitabhhelios7037No ratings yet
- Balance of Payments: Lobal ConomyDocument19 pagesBalance of Payments: Lobal ConomyMba MicNo ratings yet
- Getting To The Core: Budget AnalysisDocument37 pagesGetting To The Core: Budget AnalysisfaizanbhamlaNo ratings yet
- Highlights: Economy and Strategy GroupDocument33 pagesHighlights: Economy and Strategy GroupvladvNo ratings yet
- Introduction To European Sovereign Debt CrisisDocument8 pagesIntroduction To European Sovereign Debt CrisisVinay ArtwaniNo ratings yet
- Coordinated macroeconomic policies needed for global growthDocument7 pagesCoordinated macroeconomic policies needed for global growthddufourtNo ratings yet
- Global Recovery Stalls, Downside Risks Intensify: Figure 1. Global GDP GrowthDocument7 pagesGlobal Recovery Stalls, Downside Risks Intensify: Figure 1. Global GDP GrowthMichal ZelbaNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy Committee Meeting: Minutes of TheDocument10 pagesMonetary Policy Committee Meeting: Minutes of TheTelegraphUKNo ratings yet
- Btalk 2012 Midyear - 20120712Document45 pagesBtalk 2012 Midyear - 20120712ymahNo ratings yet
- Eco No MixDocument4 pagesEco No Mixsahilarora7190No ratings yet
- SPEX Issue 31Document13 pagesSPEX Issue 31SMU Political-Economics Exchange (SPEX)No ratings yet
- Eurozone Debt CrisisDocument19 pagesEurozone Debt CrisisVarsha AngelNo ratings yet
- June 28, 2011 July 13, 2011 June 28, 2011 June 28, 2011 January 29, 2001Document70 pagesJune 28, 2011 July 13, 2011 June 28, 2011 June 28, 2011 January 29, 2001Ilya MozyrskiyNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document94 pagesBook 1JOHNNo ratings yet
- 05 AcknowledgementDocument2 pages05 AcknowledgementNishant KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Aging and Elderly IQDocument2 pagesAging and Elderly IQ317537891No ratings yet
- MEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF ASPHYXIADocument76 pagesMEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF ASPHYXIAAl Giorgio SyNo ratings yet
- Ethamem-G1: Turn-Key Distillery Plant Enhancement With High Efficiency and Low Opex Ethamem TechonologyDocument25 pagesEthamem-G1: Turn-Key Distillery Plant Enhancement With High Efficiency and Low Opex Ethamem TechonologyNikhilNo ratings yet
- Critical Criminal Justice IssuesDocument132 pagesCritical Criminal Justice IssuesAnnamarella Amurao CardinezNo ratings yet
- Test Report OD63mm PN12.5 PE100Document6 pagesTest Report OD63mm PN12.5 PE100Im ChinithNo ratings yet
- Rapid Cycling in Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageRapid Cycling in Bipolar Disorderdo leeNo ratings yet
- AAR Maintenance 001Document3 pagesAAR Maintenance 001prakash reddyNo ratings yet
- Manual Masina de Spalat Slim SamsungDocument1,020 pagesManual Masina de Spalat Slim SamsungPerfectreviewNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour: Group ProjectDocument5 pagesConsumer Behaviour: Group ProjectAanchal MahajanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 CA 3Document13 pagesLesson 1 CA 3myndleNo ratings yet
- PB PWR e R1 PDFDocument8 pagesPB PWR e R1 PDFnallinikanth sivalankaNo ratings yet
- RA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Document2 pagesRA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Jazreth Gaile100% (1)
- Impact of Covid-19 On Audit Quality: Presented byDocument13 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On Audit Quality: Presented byMST. SADIYA SULTANANo ratings yet
- Catherineresume 2Document3 pagesCatherineresume 2api-302133133No ratings yet
- Intake Sheet SampleDocument1 pageIntake Sheet SampleRochelleNo ratings yet
- UNICESS KR Consmetics Maeteria Nunssupjara 01apr23Document44 pagesUNICESS KR Consmetics Maeteria Nunssupjara 01apr23ZB ChuaNo ratings yet
- Steam System Design RequirementsDocument29 pagesSteam System Design RequirementsAthirahNo ratings yet